Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:MIT"
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
| | | | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== [[Projects:DTIClustering|DTI Fiber Clustering and Fiber-Based Analysis]] == | == [[Projects:DTIClustering|DTI Fiber Clustering and Fiber-Based Analysis]] == | ||
Revision as of 20:44, 16 May 2008
Home < Algorithm:MITBack to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of MIT Algorithms
Our group seeks to model statistical variability of anatomy and function across subjects and between populations and to utilize computational models of such variability to improve predictions for individual subjects, as well as characterize populations. Our long-term goal is to develop methods for joint modeling of anatomy and function and to apply them in clinical and scientific studies. We work primarily with anatomical, DTI and fMRI images. We actively contribute implementations of our algorithms to the NAMIC-kit.
MIT Projects
|
Shape Based Segmentation and RegistrationThis type of algorithm assigns a tissue type to each voxel in the volume. Incorporating prior shape information biases the label assignment towards contiguous regions that are consistent with the shape model. More... New: K.M. Pohl, J. Fisher, S. Bouix, M. Shenton, R. W. McCarley, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells. Using the Logarithm of Odds to Define a Vector Space on Probabilistic Atlases. Medical Image Analysis,11(6), pp. 465-477, 2007. Best Paper Award MICCAI 2006 |
|
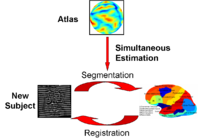
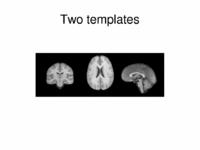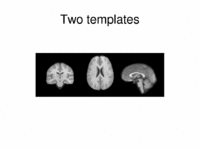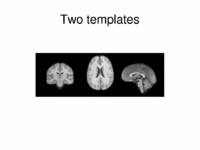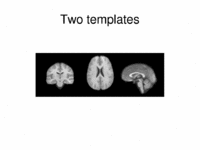
Optimal Atlas Regularization in Image SegmentationWe propose a unified framework for computing atlases from manually labeled data sets at various degrees of “sharpness” and the joint registration and segmentation of a new brain with these atlases. Using this framework, we investigate the tradeoff between warp regularization and image fidelity, i.e. the smoothness of the new subject warp and the sharpness of the atlas in a segmentation application. More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, M.R. Sabuncu, R. Desikan, B. Fischl, P. Golland. Effects of Registration Regularization and Atlas Sharpness on Segmentation Accuracy. In Proceedings of MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 683-691, 2007. MICCAI Young Scientist Award. |
|
Multimodal AtlasIn this work, we propose and investigate an algorithm that jointly co-registers a collection of images while computing multiple templates. The algorithm, called iCluster, is used to compute multiple atlases for a given population. More... New: M.R. Sabuncu, M.E. Shenton, P. Golland. Joint Registration and Clustering of Images. In Proceedings of MICCAI 2007 Statistical Registration Workshop: Pair-wise and Group-wise Alignment and Atlas Formation, 47-54, 2007. |
|
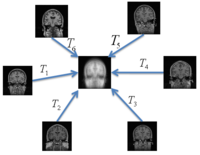
Groupwise RegistrationWe extend a previously demonstrated entropy based groupwise registration method to include a free-form deformation model based on B-splines. We provide an efficient implementation using stochastic gradient descents in a multi-resolution setting. We demonstrate the method in application to a set of 50 MRI brain scans and compare the results to a pairwise approach using segmentation labels to evaluate the quality of alignment. More... New: S.K. Balci, P. Golland, M.E. Shenton, W.M. Wells III. Free-Form B-spline Deformation Model for Groupwise Registration. In Proceedings of MICCAI 2007 Statistical Registration Workshop: Pair-wise and Group-wise Alignment and Atlas Formation, 23-30, 2007. |
|
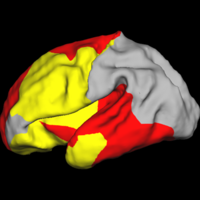
Shape Analysis With Overcomplete WaveletsIn this work, we extend the Euclidean wavelets to the sphere. The resulting over-complete spherical wavelets are invariant to the rotation of the spherical image parameterization. We apply the over-complete spherical wavelet to cortical folding development More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, W. Ou, P. Golland. On the Construction of Invertible Filter Banks on the 2-Sphere. Yeo, Ou and Golland. Accepted to the IEEE Transactions on Image Processing. P. Yu, B.T.T. Yeo, P.E. Grant, B. Fischl, P. Golland. Cortical Folding Development Study based on Over-Complete Spherical Wavelets. In Proceedings of MMBIA: IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis, 2007. |
|
fMRI clusteringIn this project we study the application of model-based clustering algorithms in identification of functional connectivity in the brain. More... New: P. Golland, Y. Golland, R. Malach. Detection of Spatial Activation Patterns As Unsupervised Segmentation of fMRI Data. In Proceedings of MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, 110-118, 2007. |

|
Joint Registration and Segmentation of DWI Fiber TractographyThe goal of this work is to jointly register and cluster DWI fiber tracts obtained from a group of subjects. More... New: U. Ziyan, M. R. Sabuncu, W. E. L. Grimson, Carl-Fredrik Westin. A Robust Algorithm for Fiber-Bundle Atlas Construction. MMBIA 2007 |
|
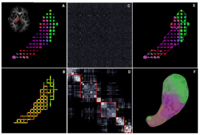
DTI Fiber Clustering and Fiber-Based AnalysisThe goal of this project is to provide structural description of the white matter architecture as a partition into coherent fiber bundles and clusters, and to use these bundles for quantitative measurement. More... New: Monica E. Lemmond, Lauren J. O'Donnell, Stephen Whalen, Alexandra J. Golby. Characterizing Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts Affected by Primary Brain Tumors. Accepted to HBM 2007. |
|
Fiber Tract Modeling, Clustering, and Quantitative AnalysisThe goal of this work is to model the shape of the fiber bundles and use this model discription in clustering and statistical analysis of fiber tracts. More... New: M. Maddah, W. E. L. Grimson, S. K. Warfield, W. M. Wells, A Unified Framework for Clustering and Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts. Medical Image Analysis, in press. M. Maddah, W. M. Wells, S. K. Warfield, C.-F. Westin, and W. E. L. Grimson, Probabilistic Clustering and Quantitative Analysis of White Matter Fiber Tracts, IPMI 2007, Netherlands. |
|
fMRI Detection and AnalysisWe are exploring algorithms for improved fMRI detection and interpretation by incorporting spatial priors and anatomical information to guide the detection. More... New: Wanmei Ou, Sandy Wells, Polina Golland. Bridging Spatial Regularization And Anatomical Priors in fMRI Detection. In preparation for submission to IEEE TMI. |
|
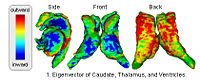
DTI-based SegmentationUnlike conventional MRI, DTI provides adequate contrast to segment the thalamic nuclei, which are gray matter structures. More... New: Ulas Ziyan, David Tuch, Carl-Fredrik Westin. Segmentation of Thalamic Nuclei from DTI using Spectral Clustering. Accepted to MICCAI 2006. |
|
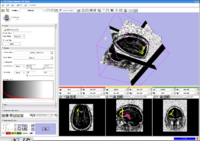
Stochastic TractographyThis work calculates posterior distributions of white matter fiber tract parameters given diffusion observations in a DWI volume. More... |
|
Population Analysis of Anatomical VariabilityOur goal is to develop mathematical approaches to modeling anatomical variability within and across populations using tools like local shape descriptors of specific regions of interest and global constellation descriptors of multiple ROI's. More... New: Mert R Sabuncu and Polina Golland. Structural Constellations for Population Analysis of Anatomical Variability.
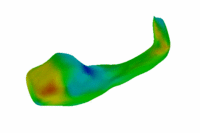
Model-Based Segmentation of Hippocampal Subfields |