Difference between revisions of "MeningiomaMRIRegistrationStudy"
From NAMIC Wiki
| Line 188: | Line 188: | ||
=Conclusions= | =Conclusions= | ||
| − | ==Limitations of the Slicer tools== | + | ==Limitations of the Slicer registration tools== |
* RigidRegistration (the following are trivial to fix in the code) | * RigidRegistration (the following are trivial to fix in the code) | ||
| Line 199: | Line 199: | ||
** Output transform should be loaded manually via Transform IO (convenience). Not trivial to fix, since RegisterImages is generic to use the same output transform for different types of registration (e.g., Rigid, Affine and BSpline), while BSpline cannot be loaded in Slicer via transform IO | ** Output transform should be loaded manually via Transform IO (convenience). Not trivial to fix, since RegisterImages is generic to use the same output transform for different types of registration (e.g., Rigid, Affine and BSpline), while BSpline cannot be loaded in Slicer via transform IO | ||
| + | |||
| + | * all of the tools implemented in Slicer require to specify the max number of iterations, which essentially requires the user to monitor convergence (metric value while iterating can be found in Slicer error log), and increase the number of iterations if the satisfactory result is not achieved. Not practical for interactive application | ||
Revision as of 18:54, 20 July 2009
Home < MeningiomaMRIRegistrationStudyContents
Objective
Accurate registration of same patient/same modality MRI data for longitudinal analysis of tumor progression.
Specific Aims
- Compare the accuracy of registration using existing Slicer and non-Slicer tools
- Identify parameter settings that produce satisfactory results
- Outline the limitations of the available registration tools in the context of the specific clinical research application
Data
- Input images: isotropic post-contrast T1 MRI acquired at different locations of BWH during 2006-2008, used under medical records study IRB. Time period between acquisition of scans for each patient is about 1 year.
- images were acquired with the same sequence, but possible on different scanners, all scans are axial
- Ground truth transformation: not available
- Expert landmarks for registration evaluation: not available
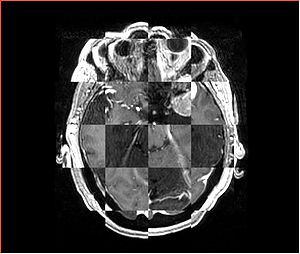
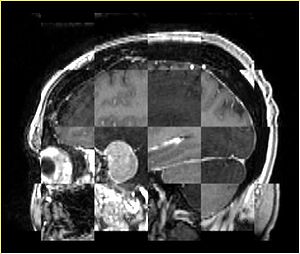
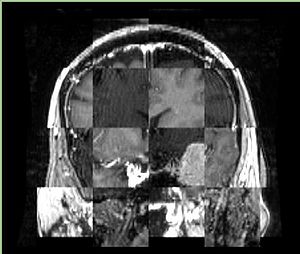
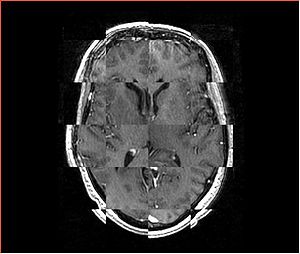
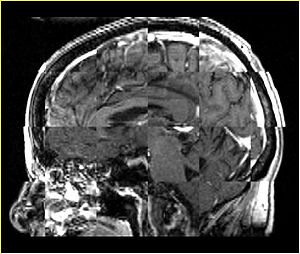
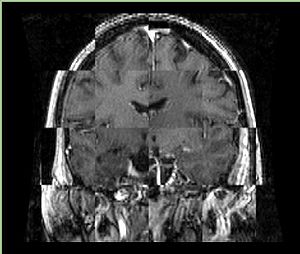
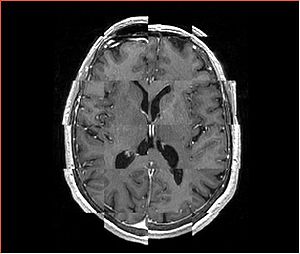
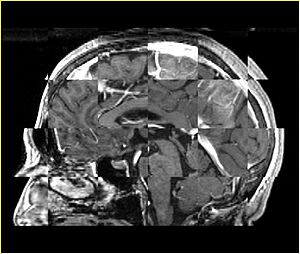
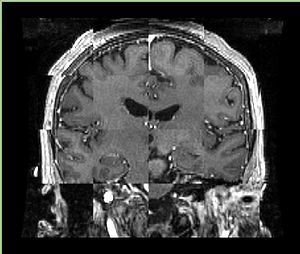
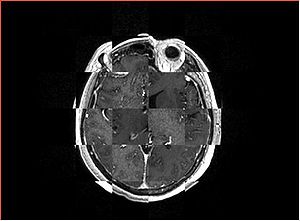
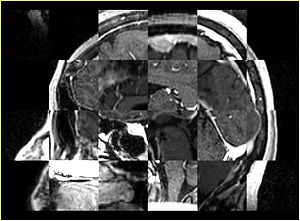
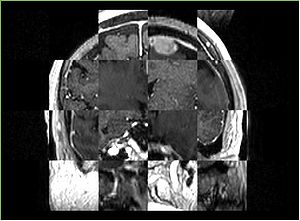
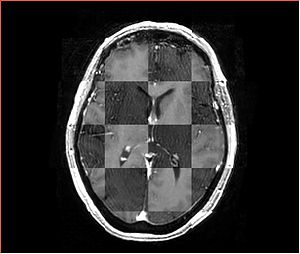
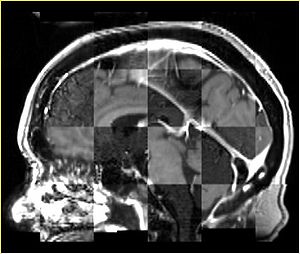
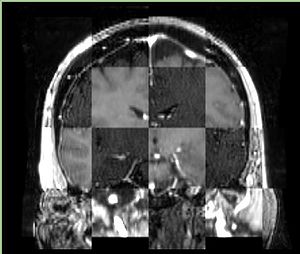
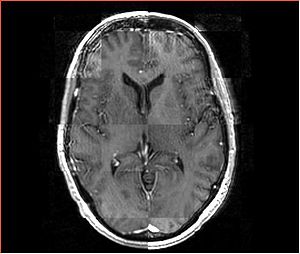
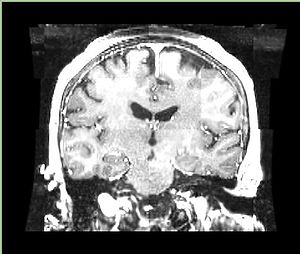
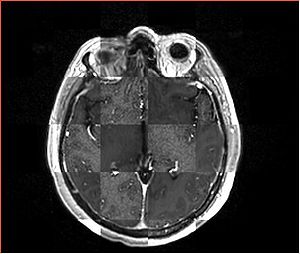
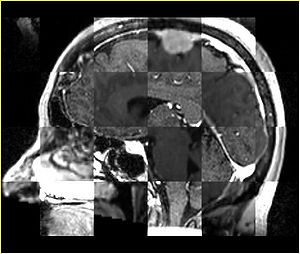
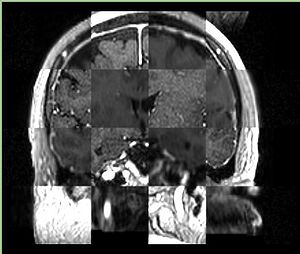
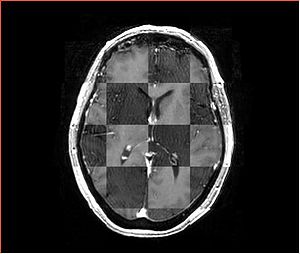
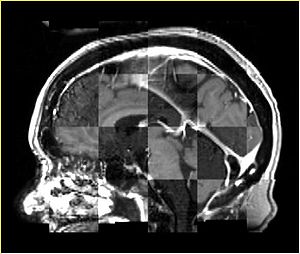
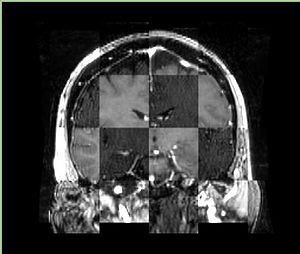
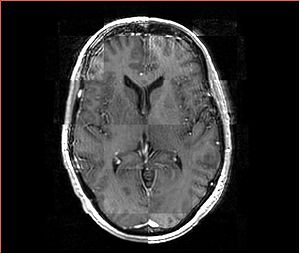
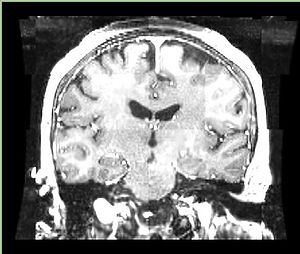
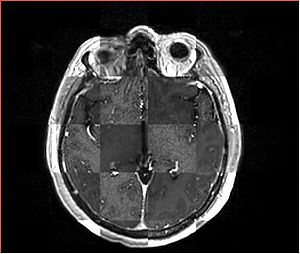
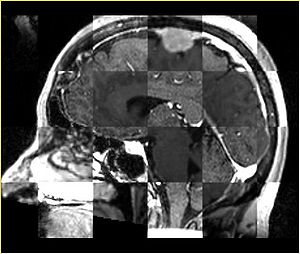
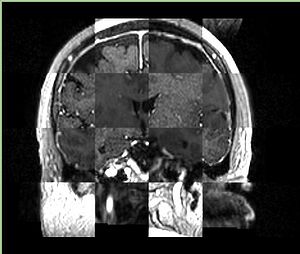
- Checkerboard appearance of unregistered images for the representative data of interest
- Case01
- Case03
- Case04
- Case10
Environment
All registration methods were executed on george.bwh.harvard.edu. Where number of threads was possible to specify, it was set to 4.
Measures of success
- qualitative assessment: visually pleasing results
- quantitative assessment: something better than "visually pleasing" (TBD)
- minimum execution time to meet the application requirements: interactive quantification of tumor growth
- minimum tuning of registration parameters (is this possible? to answer this sub-question we compare the results with FLIRT registration using its default parameters)
Methods
Registration
RegisterImages Slicer module
- parameters:
Slicer3 --launch RegisterImages --saveTransform ${RI_TFM} \
--initialization ImageCenters --registration Rigid --expectedOffset 10 \
--expectedRotation 0.1 --expectedScale 0.05 --expectedSkew 0.01 \
--verbosityLevel Standard --sampleIntensityPortion 0.05 --randomNumberSeed 12345 \
--numberOfThreads 4 --baselineNumberOfFailedPixelsTolerance 1000 \
--baselineIntensityTolerance 10 --baselineRadiusTolerance 0 --rigidMaxIterations 200 \
--rigidSamplingRatio 0.01 --affineMaxIterations 50 --affineSamplingRatio 0.02 \
--bsplineMaxIterations 20 --bsplineSamplingRatio 0.1 --controlPointSpacing 40 \
${FIXED_IMAGE} ${MOVING_IMAGE}
- execution time: ~1-2 min
RigidRegistration Slicer module
BRAINSFit
- BRAINSFit on NITRC
- Technical details on InsightJournal
- Parameters:
${SLICER} --launch BRAINSFitExe \
--fixedVolume ${TIME_POINT_1} --movingVolume ${TIME_POINT_2} \
--transformType Rigid --initializeTransformMode CenterOfHead \
--numberOfIterations 200 --numberOfSamples 100000 --minimumStepSize 0.005 \
--spatialScale 1000 --reproportionScale 1 \
--outputTransform ${BF_TRANSFORM} --histogramMatch \
--strippedOutputTransform ${BF_STRIPPED_TRANSFORM} \
--patientID ANON --studyID ANON --outputVolumePixelType float \
--backgroundFillValue 0 --maskProcessingMode ROIAUTO \
--fixedVolumeTimeIndex 0 --movingVolumeTimeIndex 0 \
--fixedVolumeOrigin 0,0,0 --movingVolumeOrigin 0,0,0 \
--medianFilterSize 0,0,0 --permitParameterVariation 1,1,1 \
--useCachingOfBSplineWeightsMode ON --useExplicitPDFDerivativesMode Whatever \
--relaxationFactor 0.5 --maximumStepSize 0.2 --failureExitCode -1 \
--fixedVolumeROI ${FIXED_IMAGE_ROI} --movingVolumeROI ${MOVING_IMAGE_ROI} \
--numberOfHistogramBins 50 --numberOfMatchPoints 10 --debugNumberOfThreads 4
Note: all parameters are the default settings except numberOfIterations (default 1500), maskProcessingMode (default NOMASK).
- execution time: ~12 min
FSL FLIRT
- FSL FLIRT
- Technical details
- parameters:
flirt -in ${TIME_POINT_2} -ref ${TIME_POINT_1} -omat ${FLIRT_TRANSFORM} -out ${RESAMPLED_IMAGE} -dof 6 -v
- execution time: ~4 min
Parameter exploration
Validation and accuracy assessment
Results
BRAINSFit
- Case01
- Case03
- Case04
- Case10
FSL FLIRT
- Case01
- Case03
- Case04
- Case10
Conclusions
Limitations of the Slicer registration tools
- RigidRegistration (the following are trivial to fix in the code)
- Number of samples is specified as an absolute value, better if it is a relative value to the total number of the image voxels
- Not possible to specify input mask, or sampling threshold for metric voxels
- Not possible to specify the number of threads, while variable number of threads used in registration may result in irreproducible results (see ITK bug #9222
- RegisterImages
- Output transform should be loaded manually via Transform IO (convenience). Not trivial to fix, since RegisterImages is generic to use the same output transform for different types of registration (e.g., Rigid, Affine and BSpline), while BSpline cannot be loaded in Slicer via transform IO
- all of the tools implemented in Slicer require to specify the max number of iterations, which essentially requires the user to monitor convergence (metric value while iterating can be found in Slicer error log), and increase the number of iterations if the satisfactory result is not achieved. Not practical for interactive application