Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:Utah"
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
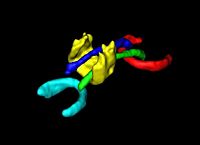
This research is a new method for constructing compact statistical point-based models of ensembles of similar shapes that does not rely on any specific surface parameterization. The method requires very little preprocessing or parameter tuning, and is applicable to a wider range of problems than existing methods, including nonmanifold surfaces and objects of arbitrary topology. [[Projects:ParticlesForShapesAndComplexes|More...]] | This research is a new method for constructing compact statistical point-based models of ensembles of similar shapes that does not rely on any specific surface parameterization. The method requires very little preprocessing or parameter tuning, and is applicable to a wider range of problems than existing methods, including nonmanifold surfaces and objects of arbitrary topology. [[Projects:ParticlesForShapesAndComplexes|More...]] | ||
| − | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> J | + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> Particle-Based Shape Analysis of Multi-object Complexes. Cates J., Fletcher P.T., Styner M., Hazlett H.C., Whitaker R. Int Conf Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008;11(Pt 1):477-485. |
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 18:35, 26 August 2009
Home < Algorithm:UtahBack to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of Utah Algorithms (PI: Ross Whitaker)
We are developing new methods in the areas of statistical shape analysis, MRI tissue segmentation, and diffusion tensor image processing and analysis. We are building shape analysis tools that can generate efficient statistical models appropriate for analyzing anatomical shape differences in the brain. We are developing a wide range of tools for diffusion tensor imaging, that span the entire pipeline from image processing to automatic white matter tract extraction to statistical testing of clinical hypotheses.
Utah Projects
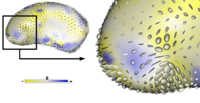
|
Adaptive, Particle-Based Sampling for Shapes and ComplexesThis research is a new method for constructing compact statistical point-based models of ensembles of similar shapes that does not rely on any specific surface parameterization. The method requires very little preprocessing or parameter tuning, and is applicable to a wider range of problems than existing methods, including nonmanifold surfaces and objects of arbitrary topology. More... New: Particle-Based Shape Analysis of Multi-object Complexes. Cates J., Fletcher P.T., Styner M., Hazlett H.C., Whitaker R. Int Conf Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2008;11(Pt 1):477-485. |
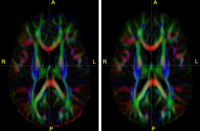
|
Diffusion Tensor Image Processing ToolsWe implement the diffusion weighted image (DWI) registration model from the paper of G.K.Rohde et al. Patient head motion and eddy currents distortion cause artifacts in maps of diffusion parameters computer from DWI. This model corrects these two distortions at the same time including brightness correction. New: We have recently developed software for eddy current correction.
|
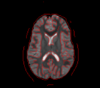 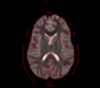
|
Correction for Geometric Distortion in Echo Planar ImagesWe have developed a variational image-based approach to correct the susceptibility artifacts in the alignment of diffusion weighted and structural MRI.The correction is formulated as an optimization of a penalty that captures the intensity difference between the jacobian corrected EPI baseline images and a corresponding T2-weighted structural image. New: R Tao, PT Fletcher, S Gerber, R Whitaker, A Variational Image-Based Approach to the Correction of Susceptibility Artifacts in the Alignment of Diffusion Weighted and Structural MRI, IPMI 2009,
|
|
DTI Volumetric White Matter ConnectivityWe have developed a PDE-based approach to white matter connectivity from DTI that is founded on the principal of minimal paths through the tensor volume. Our method computes a volumetric representation of a white matter tract given two endpoint regions. We have also developed statistical methods for quantifying the full tensor data along these pathways, which should be useful in clinical studies using DT-MRI. More... New: PT Fletcher, R Tao, W-K Jeong, RT Whitaker, A volumetric approach to quantifying region-to-region white matter connectivity in diffusion tensor MRI, IPMI 2007, pp. 346-358. |
|
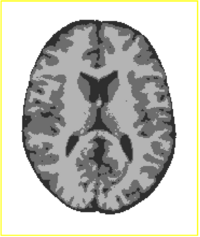
Tissue Classification with Neighborhood StatisticsWe have implemented an MRI tissue classification algorithm based on unsupervised non-parametric density estimation of tissue intensity classes. More... Suyash P. Awate, Ross T. Whitaker: Feature-Preserving MRI Denoising: A Nonparametric Empirical Bayes Approach. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 26(9): 1242-1255 (2007)
|