Difference between revisions of "OpenIGTLink"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | OpenIGTLink provides a standardized mechanism for communications among computers and devices in operating rooms (OR) for wide variety of image-guided therapy (IGT) applications. | |
| − | * | + | Examples of such applications include: |
| − | * | + | *Stereotactic surgical guidance using optical position sensor and medical image visualization software. |
| − | * | + | *Intraoperative image guidance using real-time MRI and medical image visualization software |
| − | + | *Robot-assisted intervention using robotic device and surgical planning software | |
| + | OpenIGTLink is a set of digital messaging formats and rules (or protocol) used for data exchange on a local area network (LAN). The specification of OpenIGTLink and its reference implementation, The OpenIGTLink Library, are available free of charge for any purpose including commercial use. | ||
| + | It is designed to be open, simple, platform-independent to invite users and developers from any kinds of organizations/communities and maximize the availability of OpenIGTLink-compatiple products to ease system integrations for IGT applications. An OpenIGTLink interface is available in a popular medical image processing and visualization software [http://slicer.org/ 3D Slicer]. | ||
[[OpenIGTLink/News|Recent updates.]] | [[OpenIGTLink/News|Recent updates.]] | ||
Revision as of 17:12, 12 December 2011
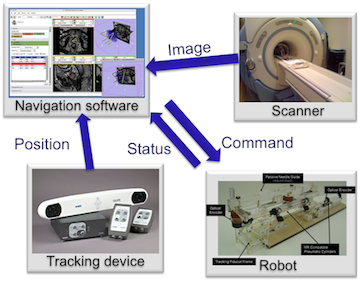
Home < OpenIGTLinkOpenIGTLink provides a standardized mechanism for communications among computers and devices in operating rooms (OR) for wide variety of image-guided therapy (IGT) applications. Examples of such applications include:
- Stereotactic surgical guidance using optical position sensor and medical image visualization software.
- Intraoperative image guidance using real-time MRI and medical image visualization software
- Robot-assisted intervention using robotic device and surgical planning software
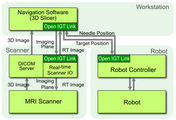
OpenIGTLink is a set of digital messaging formats and rules (or protocol) used for data exchange on a local area network (LAN). The specification of OpenIGTLink and its reference implementation, The OpenIGTLink Library, are available free of charge for any purpose including commercial use. It is designed to be open, simple, platform-independent to invite users and developers from any kinds of organizations/communities and maximize the availability of OpenIGTLink-compatiple products to ease system integrations for IGT applications. An OpenIGTLink interface is available in a popular medical image processing and visualization software 3D Slicer.
Protocol
The OpenIGTLink protocol was originally developed in 2008. In 2010, the protocol was extended with several new data type support, while maintaining backward compatibility. The new extended protocol has been released as OpenIGTLink Version 2 protocol.
OpenIGTLink Version 2
Extended Protocols
Software/Hardware
Reference Library
- The OpenIGTLink Library (C/C++)
- Matlab / Octave (under development)
Interfaces / Software
Hardware
Please see the list of hardware that supports the OpenIGTLink Protocol.
Tutorials/Events
- Tutorial Materials
- Tutorials on image-guided therapy (IGT) using Slicer 3 and OpenIGTLink are available at IGT:ToolKit
- Tutorial on 3D Slicer and Tracker simulator in 3D Slicer OpenIGTLink IF Documentation page.
- Meetings / Workshops
References
- Publications
- Tokuda J, Fischer GS, Papademetris X, Yaniv Z, Ibáñez L, Cheng P, Liu H, Blevins J, Arata J, Golby AJ, Kapur T, Pieper S, Burdette EC, Fichtinger G, Tempany CM, Hata N. OpenIGTLink: an open network protocol for image-guided therapy environment. Int J Med Robot. 2009 Dec;5(4):423-34.
- Related web pages
- Slicer 3 Image-Guided Therapy (IGT) suite
- Slicer 3 Daemon Another network interface in 3D Slicer
- OpenDMTP - Open Device Monitoring and Tracking Protocol
- Uniform Driver Interface (UDI)
- Debian Source Package: OpenIGTLink
Support
License
New BSD license ©2008 Insight Software Consortium
Mailing List / Contact
We are launching the OpenIGTLink mailing list (openigtlink@bwh.harvard.edu). If you would like to join, please subscribe from OpenIGTLink ML Info Page or send Junichi Tokuda (tokuda at bwh.harvard.edu) a message with:
- Your name
- e-mail address you would like to use to post and receive ML articles on
- Affiliation
- Your research topic
Acknowledgements
- Contributors
- Luis Ibáñez, Ph.D., Kitware, Inc.
- Junichi Tokuda, Ph.D., BWH
- Csaba Csoma, John's Hopkins University
- Jack Blevins, Acoustic MedSystems, Inc.
- Patrick Cheng, Ph.D., Georgetown University
- Haying Liu, Brigham and Women's Hospital
- Kiyoyuki Chinzei, Ph.D., National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Japan
- Jumpei Arata, Ph.D., Nagoya Institute of Technology, Japan
- Steve Pieper, Ph.D., Isomics, Inc.
- Yuichiro Hayashi, Ph.D., Nagoya University, Japan
- Atsushi Yamada, Ph.D., Nagoya Institute of Technology, Japan
- Insight Software Consortium
- Funding Support
- Enabling Technologies for MRI-Guided Prostate Interventions funded by NIH (PI: Clare Tempany, MD)
- National Center for Image-Guided Therapy (NCIGT)
- National Alliance for Medical Image Computing (NA-MIC)
- Intelligent Surgical Instrument Project sponsored by The Ministry of International Trade and Industry, Japan