Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:Utah2"
Jfishbaugh (talk | contribs) |
Jfishbaugh (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== [[Projects:GeodesicShapeRegression|Geodesic Regression for Anatomical Shape Complexes]] == | == [[Projects:GeodesicShapeRegression|Geodesic Regression for Anatomical Shape Complexes]] == | ||
| − | <font color="red">'''Ongoing (Updated 10/2014): '''</font> | + | <font color="red">'''Ongoing (Updated 10/2014): '''</font> Shape regression is of crucial importance for statistical shape analysis. It is |
| + | useful to find correlations between shape configuration and a continuous scalar parameter such as age, disease progression, drug delivery, or cognitive scores. When only few follow-up observations are available, regression is also a necessary tool to interpolate between data points and provide a scenario of continuous shape evolution over the parameter range. Longitudinal studies also require to compare such regressions across different subjects. In this project, we develop a parametric growth model for anatomical shape complexes which is the extension of scalar linear regression. | ||
[[Projects:GeodesicShapeRegression|More...]] | [[Projects:GeodesicShapeRegression|More...]] | ||
Revision as of 03:02, 14 October 2014
Home < Algorithm:Utah2Back to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of Utah 2 Algorithms (PI: Guido Gerig)
The Utah II group, guided by Guido Gerig and Marcel Prastawa, is interested in providing new methodology for analysis of DTI (including group analysis, fiber tract parametrization and quantification, longitudinal analysis), of image data including pathology (lesions (MS, lupus), tumor, trauma etc.), and methodology for registration and segmentation of serial/longitudinal image data. Methodology development will focus on subject-specific analysis in personalized medicine applications, and on providing normative data in the form of spatial altlases and descriptive information on geometric and appearance change in the presence of pathology.
Utah 2 Projects
|
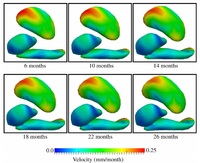
Geodesic Regression for Anatomical Shape ComplexesOngoing (Updated 10/2014): Shape regression is of crucial importance for statistical shape analysis. It is useful to find correlations between shape configuration and a continuous scalar parameter such as age, disease progression, drug delivery, or cognitive scores. When only few follow-up observations are available, regression is also a necessary tool to interpolate between data points and provide a scenario of continuous shape evolution over the parameter range. Longitudinal studies also require to compare such regressions across different subjects. In this project, we develop a parametric growth model for anatomical shape complexes which is the extension of scalar linear regression. More... Fishbaugh, J., Prastawa, M., Gerig, G., Durrleman, S. Geodesic regression of image and shape data for improved modeling of 4D trajectories. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI '14) Fishbaugh, J., Prastawa, M., Gerig, G., Durrleman, S. Geodesic image regression with a sparse parameterization of diffeomorphisms. Geometric Science of Information (GSI '13). LNCS vol 8085, pp. 95-102. (2013) Fishbaugh, J., Prastawa, M., Gerig, G., Durrleman, S. Geodesic shape regression in the framework of currents. Proc. of Information Processing in Medical Imaging (IPMI '13). Vol 23, pp. 718-729. (2013) |
|
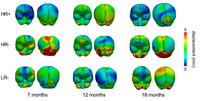
Analysis of Longitudinal Shape VariabilityOngoing (Updated 08/2012): Statistical analysis of longitudinal imaging data is crucial for understanding normal anatomical development as well as disease progression. This fundamental task is challenging due to the difficulty in modeling longitudinal changes, such as growth, and comparing changes across different populations. In this project, we develop a new method for the statistical analysis of longitudinal shape variability. More... Fishbaugh, J., Prastawa, M., Durrleman, S., Piven, J., Gerig, G. Analysis of Longitudinal Shape Variability via Subject Specific Growth Modeling. In N. Ayache et al. (Eds.): MICCAI 2012, Part I, LNCS 7510, pp. 730--737. (2012) |
|
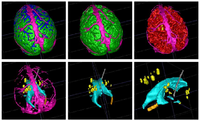
Analysis of Brain Images with Pathological ChangesOngoing: Quantification, analysis and display of brain pathology as observed in MRI is important for diagnosis, monitoring of disease progression, improved understanding of pathological processes and for studying treatment strategies. We conduct research on developing novel methodologies that covers registration, segmentation, visualization of pathological structures with the aim of quantifying changes due to lesions, bleeding, and deformations over time. More... Bo Wang, Wei Liu, Marcel Prastawa, Andrei Irimia, Paul M. Vespa, John D. Van Horn, P. Thomas Fletcher, and Guido Gerig . 4D Active Cut: An Interactive Tool for Pathological Anatomy Modeling, In Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2014 IEEE 11th International Symposium on, pp. 529-532. IEEE, 2014. |
|
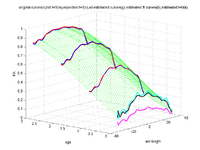
Tract-based longitudinal modeling of DTI dataThis project develops a methodology to explore subject-specific, DTI data obtained from brain's white matter tracts, available at multiple but often sparsely present timepoints. The aim is to have a continuous representation of the longitudinal diffusion changes along tract definitions. More... Sharma, A., Durrleman, S. , Gilmore, J.H. , Gerig, G. Longitudinal growth modeling of discrete-time functions with application to DTI tract evolution in early neurodevelopment. Proc. of 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI May'12), p.1397-1400. |
|
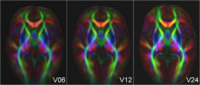
Longitudinal analysis of DWIThis project develops methodology to analyze serial/longitudinal DWI data, e.g. as baseline and follow-up in trauma, serial follow-up scans as acquired in the Huntington PREDICT study, or subject-specific white matter maturation in early brain development (see picture). More... Sharma, A., Durrleman, S. , Gilmore, J.H. , Gerig, G. Longitudinal growth modeling of discrete-time functions with application to DTI tract evolution in early neurodevelopment. Proc. of 9th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI May'12), p.1397-1400. N. Sadeghi, M. Prastawa, J. H. Gilmore, W. Lin, and G. Gerig, "Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Early Brain Development," in Proceedings IEEE Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems & Computers, Nov. 2010, in print |
|
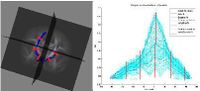
Quantitative Description of White Matter Fiber TractsAs part of this project, we are processing DTI data and computing statistics along white matter fiber tracts. For this, we are building a command line tool which allows the user to study the behavior of water diffusion along the length of the tracts. More... |

|
Smooth Growth Trajectories from Time Series Shape DataOngoing (Updated 08/16/12): Clinical research is interested in the spatiotemporal analysis of changes of anatomical shapes and structures, which potentially leads to improved understanding of the rate of change, locality and growth trajectory of structures of interest. This project develops a new methodology for the generation of a continuous growth model generated from a sparse set of shapes. More...
|
|
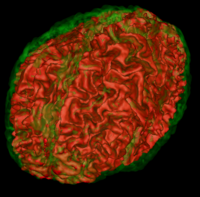
Atlas Based Brain SegmentationOngoing: Automatic segmentation can be performed reliably using priors from brain atlases and an image generative model. We have developed a tool that provides an automatic segmentation pipeline in a modular framework. Input are arbitrary number of image channels and a normative statistical brain atlas representing the population. More...
|
|
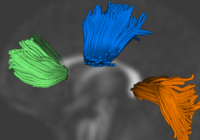
Group Analysis of DTI Fiber TractsAnalysis of populations of diffusion images typically requires time-consuming manual segmentation of structures of interest to obtain correspondance for statistics. This project uses non-rigid registration of DTI images to produce a common coordinate system for hypothesis testing of diffusion properties. More... Casey B. Goodlett, P. Thomas Fletcher, John H. Gilmore, Guido Gerig. Group Analysis of DTI Fiber Tract Statistics with Application to Neurodevelopment. NeuroImage 45 (1) Supp. 1, 2009. p. S133-S142. |
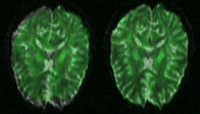
|
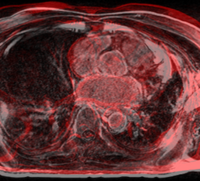
Evaluation of Registration AlgorithmsWe are interested in comparing existing registration packages to determine how registration in Slicer3 can be improved. This work focuses on examining various packages researchers are currently using for registration and comparing results on a set of examples representative of common registration tasks. More...
|
|
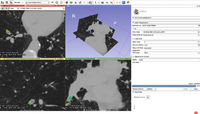
A Framework for Registration Evaluation and ExplorationIn response to the difficulties of image registration, we propose an environment where registration applications can be explored, tested, and compared. More... |
|
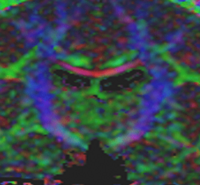
Lesion SegmentationQuantification, analysis and display of brain pathology such as white matter lesions as observed in MRI is important for diagnosis, monitoring of disease progression, improved understanding of pathological processes and for developing new therapies. More... Marcel Prastawa and Guido Gerig. Automatic MS Lesion Segmentation by Outlier Detection and Information Theoretic Region Partitioning. 3D Segmentation in the Clinic: A Grand Challenge II Workshop at Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI) 2008.
|
|
Influence of Imaging Noise on DTI StatisticsClinical acquisition of diffusion weighted images with high signal to noise ratio remains a challenge. The goal of this project is to understand the impact of MR noise on quantiative statistics of diffusion properties such as anisotropy measures, trace, etc. More... |
|
Tumor Simulation for Validating Change Tracking ApplicationsDetermining extent of pathology as it changes over time is an important clinical task. However, there is a lack of a reliable, objective ground truth for evaluating automatic tracking methods. We have developed a simulation tool that can generate MR images with known tumor and edema. More...
|