Difference between revisions of "Projects/Diffusion/Contrasting Tractography Measures"
RandyGollub (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
|- style="background:#c2c2c2; color:black" align="left" | |- style="background:#c2c2c2; color:black" align="left" | ||
| style="width:20%" | Site | | style="width:20%" | Site | ||
| − | | style="width:30%" | | + | | style="width:30%" | Algorithm |
| style="width:10%" | Input | | style="width:10%" | Input | ||
| style="width:10%" | Volumetric Output | | style="width:10%" | Volumetric Output | ||
Revision as of 19:06, 30 July 2007
Home < Projects < Diffusion < Contrasting Tractography MeasuresContents
Overview
| Site | Algorithm | Input | Volumetric Output | Geometric Output | Other Information |
| UNC | Streamline (Fiber Viewer) | DTI | None | Tracts | see here |
| Iowa | Streamline (GTract) | DTI | None | Tracts | see here |
| GaTech | Finsler Metric | DTI | None | Tracts | see here |
| BWH | Stochastic | DTI | Probability Map | None | see here |
| Utah | Volumetric Connectivity | DTI | Tracts | Tracts | see here |
| BWH | Streamline (Slicer) | DWI | None | Tracts | see here |
| BWH | Atlas Cluster | Tracts | Labelmap per bundle | Bundles | see here |
| JHU | Streamline (DTI Studio) | DWI | None | Tracts | see here |
UNC
Overview of UNC Tractography Methods
The UNC tractography measure methodology produces fiber bundles using a standard streamline tractography algorithm FiberTracking. The fiber bundles are attributed with tensor data at each point along the bundle. The user uses clustering and manual editing tools in FiberViewer to identify the fiber bundle and remove outliers. The user identifies an origin on the fiber bundle and computes statistics of the bundle as a function of arc-length along the bundle.
- Inputs
- DWI or DTI
- ROI for seed regions for tractography
- Outputs
- Fiber bundle tracts viewable in FiberViewer or Slicer3
- Summary statistics of fiber bundle as function of arc length (text file)
Iowa
The University of Iowa tractography program GTRACT is based on a modified streamlines algorithm. The advantage of this algorithm is that it helps to resolve fibers in regions where there are crossing or fanning fibers. We have also instrumented a fast marching based algorithm into GTRACT that we are currently evaluating. These algorithms require a seed region as input and will generate a VTK file representing the fiber tracts. Data associated with anisotropy, curvature or cost of the tract can be included as point data associated with the fiber tract. Tools are also available for computing the distance between fiber tracts.
- Inputs
- DWI or DTI data (DICOM or other ITK supported format)
- Parameters defining the diffusion directions
- Binary image representing the regions of interest for seeds
- Outputs
- Tensor image
- ADC and anisotropy images as defined by the user
- Fiber tracts in VTK format
GATech
Geodesic Active Contours for Fiber Tractography and Fiber Bundle Segmentation
These algorithms find the optimal path (i.e. "the anchor tract") connecting two ROIs, which is equivalent to finding a geodesic on a manifold (which may be any Finsler manifold, such as the Riemannian manifold). Then, the associated fiber bundles is segmented from the data via a region-based flow adapted for DW-MRI direction-dependent data.
- Inputs
- DWI or DTI
- ROI for seed regions (i.e. the endpoints of the fiber bundle, which most likely correspond to the associated gray matter regions)
- Outputs
- VTK files of the anchor tracts
- VTK files of the volumetric fiber bundle
- Summary statistics of fiber bundle as function of arc length (text file)
Note, I've put this together which may have some educational and/or thought provoking value. It is certainly biased towards the ideas entertained at Georgia Tech over the past few years and could be greatly extended/enhanced with more input from others in the community. Check it out here: DW-MRI Musings.
BWH
Stochastic Tractography
Stochastic Tractography is a Bayesian approach to estimating nerve fiber tracts from DWMRI (Diffusion Weighted Magnetic Imaging) images. The Bayesian framework provides a measure of confidence regarding the estimated tracts. This measure of confidence allows the algorithm to generate tracts which pass through regions with uncertain fiber directions, revealing more details about structural connectivity than non-Bayesian tractography algorithm.
- Inputs
- DWI and associated parameters (b-values, gradient directions)
- Posterior White Matter probability map
- Outputs
- Brain Connectivity Map
- Tract-Averaged FA Distribution
- Tract Length Distribution
UTAH
Volumetric connectivity information to be entered here
BWH
The DT-MRI module of Slicer uses a streamline tractography algorithm with a mutilple-ROI approach (AND and NOT operators).
- Inputs
- DWI or DTI data
- ROI
- Outputs
- Fiber tracts in VTK format
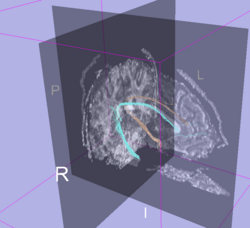
Example: Cingulum bundle generated from the validation data ROIs.
BWH
Clustering information to be entered here
Return to ContrastingTractography Project Page