Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:Past Featured Articles"
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
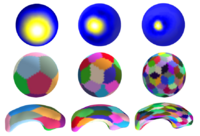
Specifically, our technique defines a multiscale parametric model of surfaces belonging to the same population using a compact set of spherical wavelets targeted to that population. We further refine the shape representation by separating into groups wavelet coefficients that describe independent global and/or local biological variations in the population, using spectral graph partitioning. We then learn a prior probability distribution induced over each group to explicitly encode these variations at different scales and spatial locations. Based on this representation, we derive a parametric active surface evolution using the multiscale prior coefficients as parameters for our optimization procedure to naturally include the prior for segmentation. Additionally, the optimization method can be applied in a coarse-to-fine manner. We apply our algorithm to two different brain structures, the caudate nucleus and the hippocampus, of interest in the study of schizophrenia. We show: 1) a reconstruction task of a test set to validate the expressiveness of our multiscale prior and 2) a segmentation task. In the reconstruction task, our results show that for a given training set size, our algorithm significantly improves the approximation of shapes in a testing set over the Point Distribution Model, which tends to oversmooth data. In the segmentation task, our validation shows our algorithm is computationally efficient and outperforms the Active Shape Model algorithm, by capturing finer shape details. | Specifically, our technique defines a multiscale parametric model of surfaces belonging to the same population using a compact set of spherical wavelets targeted to that population. We further refine the shape representation by separating into groups wavelet coefficients that describe independent global and/or local biological variations in the population, using spectral graph partitioning. We then learn a prior probability distribution induced over each group to explicitly encode these variations at different scales and spatial locations. Based on this representation, we derive a parametric active surface evolution using the multiscale prior coefficients as parameters for our optimization procedure to naturally include the prior for segmentation. Additionally, the optimization method can be applied in a coarse-to-fine manner. We apply our algorithm to two different brain structures, the caudate nucleus and the hippocampus, of interest in the study of schizophrenia. We show: 1) a reconstruction task of a test set to validate the expressiveness of our multiscale prior and 2) a segmentation task. In the reconstruction task, our results show that for a given training set size, our algorithm significantly improves the approximation of shapes in a testing set over the Point Distribution Model, which tends to oversmooth data. In the segmentation task, our validation shows our algorithm is computationally efficient and outperforms the Active Shape Model algorithm, by capturing finer shape details. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="20%" align="left" |D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum, [[Media:Nain07-spherical-wavelets.pdf|Multiscale 3-D Shape Representation and Segmentation Using Spherical Wavelets ]]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4):598-618, 2007. | + | | width="20%" align="left" || |
| + | ||D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum, [[Media:Nain07-spherical-wavelets.pdf|Multiscale 3-D Shape Representation and Segmentation Using Spherical Wavelets ]]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4):598-618, 2007. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
| align="left" valign="top" | A statistical model is presented that combines the registration of an atlas with the segmentation of magnetic resonance images. We use an Expectation Maximization-based algorithm to find a solution within the model, which simultaneously estimates image artifacts, anatomical labelmaps, and a structure-dependent hierarchical mapping from the atlas to the image space. The algorithm produces segmentations for brain tissues as well as their substructures. We demonstrate the approach on a set of 22 magnetic resonance images. On this set of images, the new approach performs significantly better than similar methods which sequentially apply registration and segmentation. | | align="left" valign="top" | A statistical model is presented that combines the registration of an atlas with the segmentation of magnetic resonance images. We use an Expectation Maximization-based algorithm to find a solution within the model, which simultaneously estimates image artifacts, anatomical labelmaps, and a structure-dependent hierarchical mapping from the atlas to the image space. The algorithm produces segmentations for brain tissues as well as their substructures. We demonstrate the approach on a set of 22 magnetic resonance images. On this set of images, the new approach performs significantly better than similar methods which sequentially apply registration and segmentation. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | width="20%" align="left" |K. M. Pohl, J. Fisher, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells, [[Media:Pohl-NeuroImage-06.pdf| A Bayesian Model for Joint Segmentation and Registration]]. NeuroImage, 31(1):228-239, 2006. | + | | width="20%" align="left" || |
| + | ||K. M. Pohl, J. Fisher, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells, [[Media:Pohl-NeuroImage-06.pdf| A Bayesian Model for Joint Segmentation and Registration]]. NeuroImage, 31(1):228-239, 2006. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 20:30, 22 August 2009
Home < Algorithm:Past Featured ArticlesBack to NA-MIC Algorithms
| This paper presents a novel multiscale shape representation and segmentation algorithm based on the spherical wavelet transform. This work is motivated by the need to compactly and accurately encode variations at multiple scales in the shape representation in order to drive the segmentation and shape analysis of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. Our proposed shape representation can be optimized to compactly encode shape variations in a population at the needed scale and spatial locations, enabling the construction of more descriptive, nonglobal, nonuniform shape probability priors to be included in the segmentation and shape analysis framework. In particular, this representation addresses the shortcomings of techniques that learn a global shape prior at a single scale of analysis and cannot represent fine, local variations in a population of shapes in the presence of a limited dataset.
Specifically, our technique defines a multiscale parametric model of surfaces belonging to the same population using a compact set of spherical wavelets targeted to that population. We further refine the shape representation by separating into groups wavelet coefficients that describe independent global and/or local biological variations in the population, using spectral graph partitioning. We then learn a prior probability distribution induced over each group to explicitly encode these variations at different scales and spatial locations. Based on this representation, we derive a parametric active surface evolution using the multiscale prior coefficients as parameters for our optimization procedure to naturally include the prior for segmentation. Additionally, the optimization method can be applied in a coarse-to-fine manner. We apply our algorithm to two different brain structures, the caudate nucleus and the hippocampus, of interest in the study of schizophrenia. We show: 1) a reconstruction task of a test set to validate the expressiveness of our multiscale prior and 2) a segmentation task. In the reconstruction task, our results show that for a given training set size, our algorithm significantly improves the approximation of shapes in a testing set over the Point Distribution Model, which tends to oversmooth data. In the segmentation task, our validation shows our algorithm is computationally efficient and outperforms the Active Shape Model algorithm, by capturing finer shape details. | ||
| width="20%" align="left" | D. Nain, S. Haker, A. Bobick, A. Tannenbaum, Multiscale 3-D Shape Representation and Segmentation Using Spherical Wavelets . IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 26(4):598-618, 2007. |
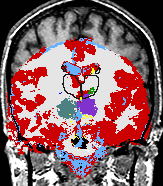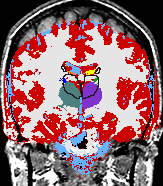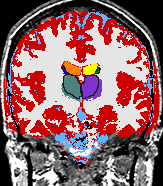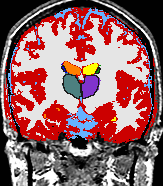
- K. M. Pohl et al. A Bayesian Model for Joint Segmentation and Registration
|
A statistical model is presented that combines the registration of an atlas with the segmentation of magnetic resonance images. We use an Expectation Maximization-based algorithm to find a solution within the model, which simultaneously estimates image artifacts, anatomical labelmaps, and a structure-dependent hierarchical mapping from the atlas to the image space. The algorithm produces segmentations for brain tissues as well as their substructures. We demonstrate the approach on a set of 22 magnetic resonance images. On this set of images, the new approach performs significantly better than similar methods which sequentially apply registration and segmentation. | |
| width="20%" align="left" | K. M. Pohl, J. Fisher, W.E.L. Grimson, R. Kikinis, and W.M. Wells, A Bayesian Model for Joint Segmentation and Registration. NeuroImage, 31(1):228-239, 2006. |