Difference between revisions of "Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C08"
From NAMIC Wiki
(Created page with 'Back to ARRA main page <br> Back to Registration main page <br> [[Projects:RegistrationDocumentation:UseCaseInv…') |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
{| style="color:#bbbbbb; background-color:#333333;" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="0" | {| style="color:#bbbbbb; background-color:#333333;" cellpadding="10" cellspacing="0" border="0" | ||
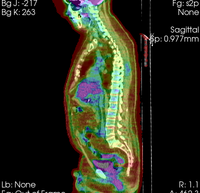
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:RegLib_C08_WholeBodyPET-CT1.png|200px|lleft|this is the fixed reference image. All images are aligned into this space]] |
|[[Image:Arrow_left_gray.jpg|100px|lleft]] | |[[Image:Arrow_left_gray.jpg|100px|lleft]] | ||
| − | |[[Image: | + | |[[Image:RegLib_C08_WholeBodyPET-CT2.png|200px|lleft|this is the moving image. The transform is calculated by matching this to the reference image]] |
|align="left"|LEGEND<br> | |align="left"|LEGEND<br> | ||
[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the reference image that is fixed and does not move. All other images are aligned into this space and resolution<br> | [[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the reference image that is fixed and does not move. All other images are aligned into this space and resolution<br> | ||
[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the moving image that determines the registration transform. <br> | [[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|20px|lleft]] this indicates the moving image that determines the registration transform. <br> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|40px|lleft]] | + | |[[Image:Button_red_fixed.jpg|40px|lleft]] whole body CT + PET baseline |
| | | | ||
| − | |[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|40px|lleft]] | + | |[[Image:Button_green_moving.jpg|40px|lleft]] whole body CT + PET follow-up |
|- | |- | ||
| − | |0. | + | |CT: <small> 512 x 512 x 267<br> 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm<br> PET: 128 x 128 x 267<br> 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm </small> |
| | | | ||
| − | |0. | + | |CT: <small>512 x 512 x 195<br> 0.98 x 0.98 x 5.0 mm<br> PET: 168 x 168 x 195<br> 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm </small> |
|} | |} | ||
===Objective / Background === | ===Objective / Background === | ||
| − | + | Change assessment. | |
=== Keywords === | === Keywords === | ||
| − | + | PET-CT, whole-body, change assessment | |
===Input Data=== | ===Input Data=== | ||
| − | *[[Image:Button_red_fixed_white.jpg|20px]]reference/fixed : | + | *[[Image:Button_red_fixed_white.jpg|20px]]reference/fixed : baseline CT: 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm , PET: 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm |
| − | *[[Image:Button_green_moving_white.jpg|20px]] moving: | + | *[[Image:Button_green_moving_white.jpg|20px]] moving: CT: 0.98 x 0.98 x 5; PET: 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm |
=== Registration Results=== | === Registration Results=== | ||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Download === | ===Download === | ||
| − | *'''[[Media: | + | *'''[[Media:RegLib_C08_WholeBody_PET-CT.zip|download entire package <small> (Data,Presets,Tutorial, Solution, zip file 135 MB) </small>]]''' |
<!-- | <!-- | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
=== Discussion: Registration Challenges === | === Discussion: Registration Challenges === | ||
*accuracy is the critical criterion here. We need the registration error (residual misalignment) to be smaller than the change we want to measure/detect. Agreement on what constitutes good alignment can therefore vary greatly. | *accuracy is the critical criterion here. We need the registration error (residual misalignment) to be smaller than the change we want to measure/detect. Agreement on what constitutes good alignment can therefore vary greatly. | ||
| − | *the two | + | *the two series have different voxel sizes |
| − | + | *images are large volumes (>100 MB total) | |
| − | * | + | *image content reaches border of image on two sides |
=== Discussion: Key Strategies === | === Discussion: Key Strategies === | ||
*the two images have identical contrast, hence we consider "sharper" cost functions, such as NormCorr or MeanSqrd | *the two images have identical contrast, hence we consider "sharper" cost functions, such as NormCorr or MeanSqrd | ||
*we have aliasing at the image margins that should be masked out | *we have aliasing at the image margins that should be masked out | ||
| − | *the two images are | + | *the two images are far apart initially, we will need some form of initialization |
| − | |||
*because accuracy is more important than speed here, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%. | *because accuracy is more important than speed here, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%. | ||
*we also expect minimal differences in scale & distortion: so we can either set the expected values to 0 or run a rigid registration | *we also expect minimal differences in scale & distortion: so we can either set the expected values to 0 or run a rigid registration | ||
*we test the result in areas with good anatomical detail and contrast, far away from the pathology. With rigid body motion a local measure of registration accuracy is representative and can give us a valid limit of detectable change. | *we test the result in areas with good anatomical detail and contrast, far away from the pathology. With rigid body motion a local measure of registration accuracy is representative and can give us a valid limit of detectable change. | ||
Revision as of 22:33, 3 February 2010
Home < Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C08Back to ARRA main page
Back to Registration main page
Back to Registration Use-case Inventory
Contents
Slicer Registration Use Case Exampe #8: Intra-subject whole-body PET-CT
Objective / Background
Change assessment.
Keywords
PET-CT, whole-body, change assessment
Input Data
 reference/fixed : baseline CT: 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm , PET: 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm
reference/fixed : baseline CT: 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm , PET: 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm moving: CT: 0.98 x 0.98 x 5; PET: 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm
moving: CT: 0.98 x 0.98 x 5; PET: 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm
Registration Results
Download
Discussion: Registration Challenges
- accuracy is the critical criterion here. We need the registration error (residual misalignment) to be smaller than the change we want to measure/detect. Agreement on what constitutes good alignment can therefore vary greatly.
- the two series have different voxel sizes
- images are large volumes (>100 MB total)
- image content reaches border of image on two sides
Discussion: Key Strategies
- the two images have identical contrast, hence we consider "sharper" cost functions, such as NormCorr or MeanSqrd
- we have aliasing at the image margins that should be masked out
- the two images are far apart initially, we will need some form of initialization
- because accuracy is more important than speed here, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%.
- we also expect minimal differences in scale & distortion: so we can either set the expected values to 0 or run a rigid registration
- we test the result in areas with good anatomical detail and contrast, far away from the pathology. With rigid body motion a local measure of registration accuracy is representative and can give us a valid limit of detectable change.