Difference between revisions of "Algorithm:MIT"
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
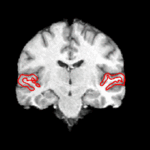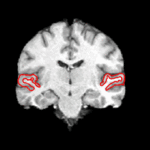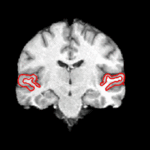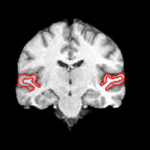
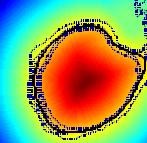
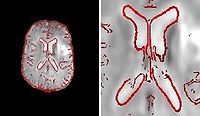
We are interested in developing computational methods for the assimilation of magnetic resonance image data into physiological models of glioma - the most frequent primary brain tumor - for a patient-adaptive modeling of tumor growth. [[Projects:TumorModeling|More...]] | We are interested in developing computational methods for the assimilation of magnetic resonance image data into physiological models of glioma - the most frequent primary brain tumor - for a patient-adaptive modeling of tumor growth. [[Projects:TumorModeling|More...]] | ||
| − | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> B. Menze, K. Van Leemput, D. Lashkari, M.A. Weber, N. Ayache, and P. Golland. A Generative Model for Brain Tumor Segmentation in Multi-modal Images. | + | <font color="red">'''New: '''</font> B. Menze, K. Van Leemput, D. Lashkari, M.A. Weber, N. Ayache, and P. Golland. A Generative Model for Brain Tumor Segmentation in Multi-modal Images. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 6362:151-159, 2010. |
Revision as of 18:44, 5 November 2010
Home < Algorithm:MITBack to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of MIT Algorithms (PI: Polina Golland)
Our group seeks to model statistical variability of anatomy and function across subjects and between populations and to utilize computational models of such variability to improve predictions for individual subjects, as well as characterize populations. Our long-term goal is to develop methods for joint modeling of anatomy and function and to apply them in clinical and scientific studies. We work primarily with anatomical, DTI and fMRI images. We actively contribute implementations of our algorithms to the NAMIC-kit.
MIT Projects
|
Nonparametric Models for Supervised Image SegmentationWe propose a non-parametric, probabilistic model for the automatic segmentation of medical images, given a training set of images and corresponding label maps. The resulting inference algorithms we develop rely on pairwise registrations between the test image and individual training images. The training labels are then transferred to the test image and fused to compute a final segmentation of the test subject. More... New: M.R. Sabuncu, B.T.T Yeo, K. Van Leemput, B. Fischl, and P. Golland. A Generative Model for Image Segmentation Based on Label Fusion. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, in Press. New: M.R. Sabuncu, B.T.T Yeo, K. Van Leemput, B. Fischl, and P. Golland. Supervised Nonparametric Image Parcellation. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 5762:1075-1083, 2009. New: M.R. Sabuncu, B.T.T. Yeo, K. Van Leemput, B. Fischl, and P. Golland. Nonparametric Mixture Models for Supervised Image Parcellation. In Proc. MICCAI Workshop on Probabilistic Models for Medical Image Analysis, 301-313, 2009. |
Joint Segmentation of Image Ensembles via Latent AtlasesSpatial priors, such as probabilistic atlases, play an important role in MRI segmentation. The atlases are typically generated by averaging manual labels of aligned brain regions across different subjects. However, the availability of comprehensive, reliable and suitable manual segmentations is limited. We therefore propose a joint segmentation of corresponding, aligned structures in the entire population that does not require a probability atlas. More... New: T. Riklin Raviv, K. Van-Leemput, B.M. Menze, W.M. Wells III, and P. Golland. Joint Segmentation of Image Ensembles via Latent Atlases, Special Issue of Medical Image Analysis (MedIA), 2010 New: T. Riklin Raviv, K. Van Leemput, W.M. Wells III and P. Golland, Joint Segmentation of Image Ensembles via Latent Atlases, In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 5761:272-280, 2009. Young Investigator Award. New: T. Riklin Raviv, B.H. Menze, K. Van Leemput, B. Stieltjes, M.A. Weber, N. Ayache, W. M. Wells III and P. Golland, Joint Segmentation using Patient specific Latent Anatomy Model. In Proc. MICCAI Workshop on Probabilistic Models for Medical Image Analysis, 244-255, 2009.
| |
|
Cardiac Ablation Scar SegmentationCatheter radio-frequency (RF) ablation is a technique used to treat atrial fibrillation, a very common heart condition. The objective of this project is to automatically segment the scar created by RF ablation in delayed enhancement MR images acquired after the procedure. This will then provide surgeons with a visualization which will help them to rapidly evaluate the success of the procedure. More...
|
Brain Tumor Segmentation and ModelingWe are interested in developing computational methods for the assimilation of magnetic resonance image data into physiological models of glioma - the most frequent primary brain tumor - for a patient-adaptive modeling of tumor growth. More... New: B. Menze, K. Van Leemput, D. Lashkari, M.A. Weber, N. Ayache, and P. Golland. A Generative Model for Brain Tumor Segmentation in Multi-modal Images. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 6362:151-159, 2010.
|
|
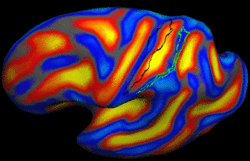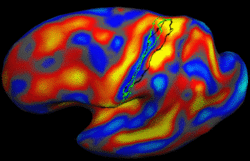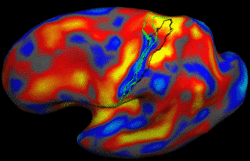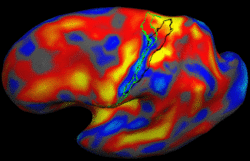
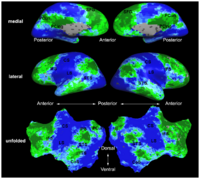
Learning Task-Optimal Registration Cost FunctionsWe present a framework for learning the parameters of registration cost functions. The parameters of the registration cost function -- for example, the tradeoff between the image similarity and regularization terms -- are typically determined manually through inspection of the image alignment and then fixed for all applications. We propose a principled approach to learn these parameters with respect to particular applications. More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, M.R. Sabuncu, T. Vercauteren, D. Holt, K. Amunts, K. Zilles, P. Golland, and B. Fischl. Learning Task-Optimal Registration Cost Functions for Localizing Cytoarchitecture and Function in the Cerebral Cortex. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(7):1424-1441, 2010. New: B.T.T. Yeo, M. Sabuncu, P. Golland, B. Fischl. Task-Optimal Registration Cost Functions. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 5761:598-606, 2009. |
|
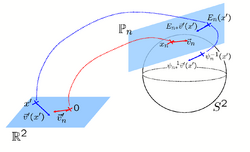
Spherical Demons: Fast Surface RegistrationWe present the fast Spherical Demons algorithm for registering two spherical images. By exploiting spherical vector spline interpolation theory, we show that a large class of regularizers for the modified demons objective function can be efficiently approximated on the sphere using convolution. Based on the one parameter subgroups of diffeomorphisms, More... New: B.T.T. Yeo, M.R. Sabuncu, T. Vercauteren, N. Ayache, B. Fischl and P. Golland. Spherical Demons: Fast Diffeomorphic Landmark-Free Surface Registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 29(3):650-668, 2010.
|
|
Fieldmap-Free EPI Distortion CorrectionIn this project we aim to improve the EPI distortion correction algorithms. More... New: Poynton C., Jenkinson M., Wells III W. Atlas-Based Improved Prediction of Magnetic Field Inhomogeneity for Distortion Correction of EPI Data. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 5761:951-959, 2009. |
|
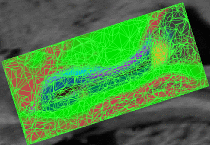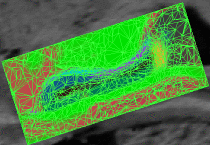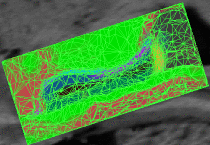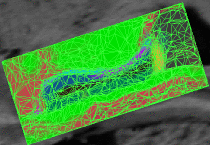
fMRI clusteringIn this project we study the application of model-based clustering algorithms in identification of functional connectivity in the brain. More... New: A. Venkataraman, Y. Rathi, M. Kubicki, C-F. Westin and P. Golland. Joint Generative Model for fMRI/DWI and its Application to Population Studies. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 6361:191-199, 2010. New: D. Lashkari, E. Vul, N.G. Kanwisher, and P. Golland. Discovering structure in the space of fMRI selectivity profiles. NeuroImage, 3(15):1085-1098, 2010. New: A. Venkataraman, M. Kubicki, C.-F. Westin, and P. Golland. Robust Feature Selection in Resting-State fMRI Connectivity Based on Population Studies. In Proc. MMBIA: IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis, 2010. New: D. Lashkari, R. Sridharan, E. Vul, P.-J. Hsieh, N. Kanwisher, and P. Golland. Nonparametric Hierarchical Bayesian Model for Functional Brain Parcellation. In Proc. MMBIA: IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Mathematical Methods in Biomedical Image Analysis, 2010. New: A. Venkataraman, K.R.A Van Dijk, R.L. Buckner, and P. Golland. Exploring functional connectivity in fMRI via clustering. In Proc. ICASSP: IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 441-444, 2009. New: D. Lashkari and P. Golland. Exploratory fMRI Analysis without Spatial Normalization. In Proc. IPMI: International Conference on Information Processing and Medical Imaging, LNCS 5636:398-410, 2009. Honorable Mention for the Erbsmann Award. |
|
Bayesian Segmentation of MRI ImagesThe aim of this project is to develop, implement, and validate a generic method for segmenting MRI images that automatically adapts to different acquisition sequences. More... New: K. Van Leemput, A. Bakkour, T. Benner, G. Wiggins, L.L. Wald, J. Augustinack, B.C. Dickerson, P. Golland, and B. Fischl. Automated Segmentation of Hippocampal Subfields from Ultra-High Resolution In Vivo MRI. Hippocampus, 19:549-557, 2009. New: K. Van Leemput. Encoding Probabilistic Atlases Using Bayesian Inference. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28(6):822-837, 2009.
|
|
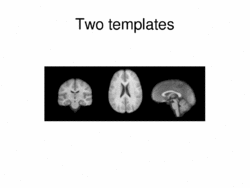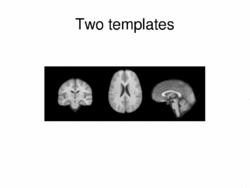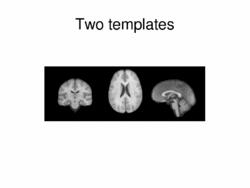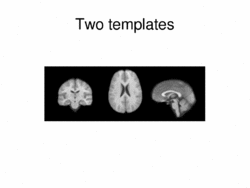
Multimodal AtlasIn this work, we propose and investigate an algorithm that jointly co-registers a collection of images while computing multiple templates. The algorithm, called iCluster, is used to compute multiple atlases for a given population. More... New: Image-driven Population Analysis through Mixture-Modeling, M.R. Sabuncu, S.K. Balci, M.E. Shenton and P. Golland. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 28(9):1473 - 1487, 2009.
|
|
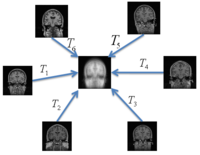
Groupwise RegistrationWe extend a previously demonstrated entropy based groupwise registration method to include a free-form deformation model based on B-splines. We provide an efficient implementation using stochastic gradient descents in a multi-resolution setting. We demonstrate the method in application to a set of 50 MRI brain scans and compare the results to a pairwise approach using segmentation labels to evaluate the quality of alignment. In a related project, we develop a method that reconciles the practical advantages of symmetric registration with the asymmetric nature of image-template registration by adding a simple correction factor to the symmetric cost function. We instantiate our model within a log-domain diffeomorphic registration framework. Our experiments show exploiting the asymmetry in image-template registration improves alignment in the image coordinates. More... New: Asymmetric Image-Template Registration, M.R. Sabuncu, B.T. Thomas Yeo, T. Vercauteren, K. Van Leemput, P. Golland. In Proc. MICCAI: International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention, LNCS 5761:565-573, 2009.
|
|
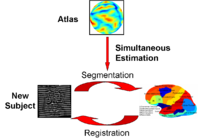
Optimal Atlas Regularization in Image SegmentationWe propose a unified framework for computing atlases from manually labeled data sets at various degrees of “sharpness” and the joint registration and segmentation of a new brain with these atlases. Using this framework, we investigate the tradeoff between warp regularization and image fidelity, i.e. the smoothness of the new subject warp and the sharpness of the atlas in a segmentation application. More... |
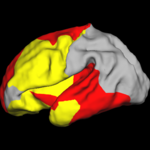
|
Shape Analysis With Overcomplete WaveletsIn this work, we extend the Euclidean wavelets to the sphere. The resulting over-complete spherical wavelets are invariant to the rotation of the spherical image parameterization. We apply the over-complete spherical wavelet to cortical folding development More... |
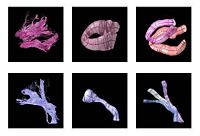
|
Fiber Tract Modeling, Clustering, and Quantitative AnalysisThe goal of this work is to model the shape of the fiber bundles and use this model description in clustering and statistical analysis of fiber tracts. More... |
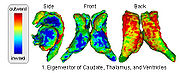
|
Shape Based Segmentation and RegistrationThis type of algorithm assigns a tissue type to each voxel in the volume. Incorporating prior shape information biases the label assignment towards contiguous regions that are consistent with the shape model. More... |

|
Joint Registration and Segmentation of DWI Fiber TractographyThe goal of this work is to jointly register and cluster DWI fiber tracts obtained from a group of subjects. More... |
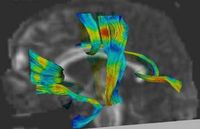
|
DTI Fiber Clustering and Fiber-Based AnalysisThe goal of this project is to provide structural description of the white matter architecture as a partition into coherent fiber bundles and clusters, and to use these bundles for quantitative measurement. More... |
|
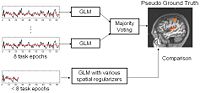
fMRI Detection and AnalysisWe are exploring algorithms for improved fMRI detection and interpretation by incorporting spatial priors and anatomical information to guide the detection. More... |
|
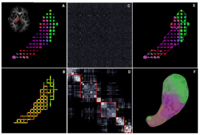
DTI-based SegmentationUnlike conventional MRI, DTI provides adequate contrast to segment the thalamic nuclei, which are gray matter structures. More... |
|
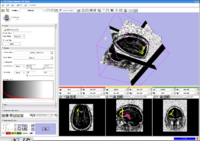
Stochastic TractographyThis work calculates posterior distributions of white matter fiber tract parameters given diffusion observations in a DWI volume. More... |
|
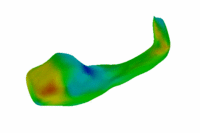
Population Analysis of Anatomical VariabilityOur goal is to develop mathematical approaches to modeling anatomical variability within and across populations using tools like local shape descriptors of specific regions of interest and global constellation descriptors of multiple ROI's. More... |