Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C27
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C27v3.6.1
Back to ARRA main page
Back to Registration main page
Back to Registration Use-case Inventory
v3.6.1  Slicer Registration Library Exampe #27: Diffusion Weighted Image Volume: align with structural reference MRI
Slicer Registration Library Exampe #27: Diffusion Weighted Image Volume: align with structural reference MRI
Input
|
|
|
|
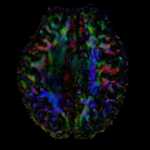
|
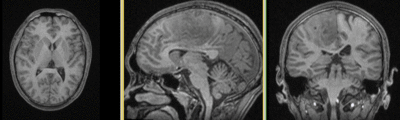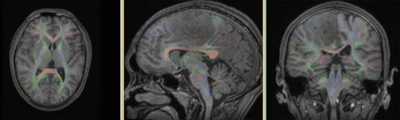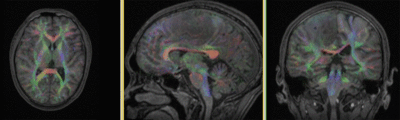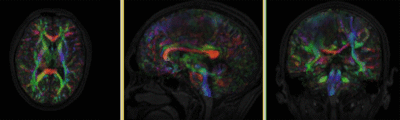
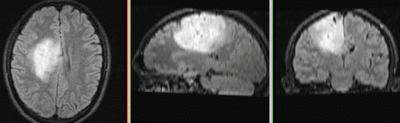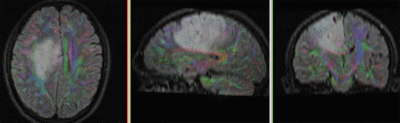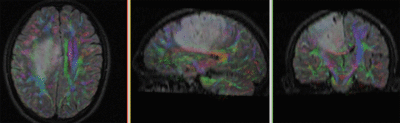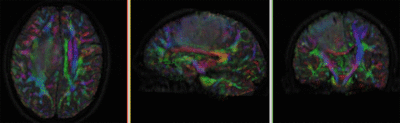
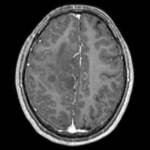
| fixed image/target T1 |
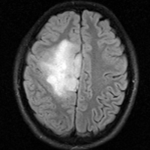
fixed image/target FLAIR |
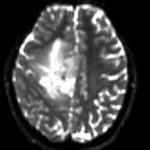
moving image 2a DTI baseline |
moving image 2b DTI tensor |
Modules
- Slicer 3.6.1 recommended modules: BrainsFit
Objective / Background
This is a typical example of DTI processing. Goal is to align the DTI image with a structural scan that provides accuracte anatomical reference. The DTI contains acquisition-related distortion and insufficient contrast to discern anatomical detail. For treatment planning and evaluation, location of functionally critical fiber tracts relative to the pathology is sought.
Keywords
MRI, brain, head, intra-subject, DTI, DWI
Input Data
- reference/fixed : T1 axial, 0.98 x 0.98 x 1 , 192 x 256 x 176
- reference/fixed : FLAIR axial, 0.4mm resolution in plane, 4mm slices, 448 x 512 x 30
- moving: Baseline image of acquired DTI volume, corresponds to T2w MRI , 1.96 x 1.96 x 3 mm voxel size, oblique, 128 x 128 x 40
- moving: Tensor data of DTI volume, oblique, same orientation as Baseline image. The result Xform will be applied to this volume. The original DWI has 64 directions, the extracted DTI volume has 9 scalars, i.e. 128 x 128 x 40 x 9
Registration Results
Download
- Data
- Presets
- Documentation
Discussion: Registration Challenges
- The DTI contains acquisition-related distortions (commonly EPI acquisitions) that can make automated registration difficult.
- the two images often have strong differences in voxel sizes and voxel anisotropy. If the orientation of the highest resolution is not the same in both images, finding a good match can be difficult.
- there is widespread and extensive pathology in the right hemisphere that might affect the registration if contrast is different between the baseline and structural reference scan.
Discussion: Key Strategies
- because the pathology appears similar in the FLAIR as in the DTI baseline, we choose the FLAIR as reference
- masking is likely necessary to obtain good results.
- in this example the initial alignment of the two scans is pretty good already. No initial affine alignment is needed.
- these two images are not too far apart initially, so we reduce the default of expected translational misalignment
- because speed is not that critical, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%.