Algorithm:GATech
Back to NA-MIC Algorithms
Overview of Georgia Tech Algorithms (PI: Allen Tannenbaum)
At Georgia Tech, we are broadly interested in a range of mathematical image analysis algorithms for segmentation, registration, diffusion-weighted MRI analysis, and statistical analysis. For many applications, we cast the problem in an energy minimization framework wherein we define a partial differential equation whose numeric solution corresponds to the desired algorithmic outcome. The following are many examples of PDE techniques applied to medical image analysis.
Georgia Tech Projects
|
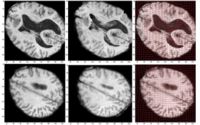
Optimal Mass Transport RegistrationThe goal of this project is to implement a computationaly efficient Elastic/Non-rigid Registration algorithm based on the Monge-Kantorovich theory of optimal mass transport for 3D Medical Imagery. Our technique is based on Multigrid and Multiresolution techniques. This method is particularly useful because it is parameter free and utilizes all of the grayscale data in the image pairs in a symmetric fashion and no landmarks need to be specified for correspondence. More... New: Tauseef ur Rehman, A. Tannenbaum. Multigrid Optimal Mass Transport for Image Registration and Morphing. SPIE Conference on Computational Imaging V, Jan 2007. |
|
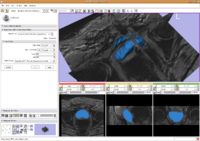
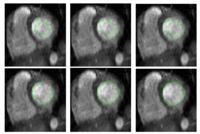
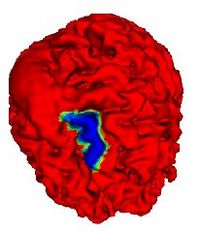
Prostate SegmentationThe 3D prostate MRI images are collected by collaborators at Queen’s University. With a little manual initialization, the algorithm provided the results give to the left. The method mainly uses Random Walk algorithm. More... New: Segmentation tool put into Slicer3.
|
|
Particle Filter Registration of Medical Imagery3D volumetric image registration is performed. The method is based on registering the images through point sets, which is able to handle long distance between as well as registration between Supine and Prone pose prostate. More... New: Will be put into Slicer3. |

|
Tubular Surface Segmentation FrameworkWe have proposed a new model for tubular surfaces that transforms the problem of detecting a surface in 3D space, to detecting a curve in 4D space. Besides allowing us to impose a "soft" tubular shape prior, this also leads to computational efficiency over conventional surface segmentation approaches. More...
|
|
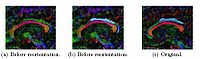
Re-Orientation Approach for Segmentation of DW-MRIThis work proposes a methodology to segment tubular fiber bundles from diffusion weighted magnetic resonance images (DW-MRI). Segmentation is simplified by locally reorienting diffusion information based on large-scale fiber bundle geometry. More... New: Near-tubular fiber bundle segmentation for diffusion weighted imaging: segmentation through frame reorientation. Neuroimage, Mar 2009. |
|
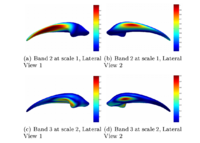
Multiscale Shape Segmentation TechniquesTo represent multiscale variations in a shape population in order to drive the segmentation of deep brain structures, such as the caudate nucleus or the hippocampus. More... |
|
Geodesic Tractography SegmentationIn this work, we provide an energy minimization framework which allows one to find fiber tracts and volumetric fiber bundles in brain diffusion-weighted MRI (DW-MRI). More... New: J. Melonakos, E. Pichon, S. Angenet, and A. Tannenbaum. Finsler Active Contours. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, March 2008, Vol 30, Num 3. |

|
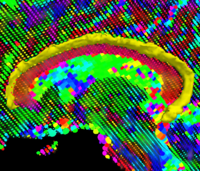
Wavelet Shrinkage for Shape AnalysisShape analysis has become a topic of interest in medical imaging since local variations of a shape could carry relevant information about a disease that may affect only a portion of an organ. We developed a novel wavelet-based denoising and compression statistical model for 3D shapes. More... |
|
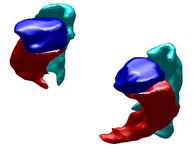
Label Space: A Coupled Multi-Shape RepresentationMany techniques for multi-shape representation may often develop inaccuracies stemming from either approximations or inherent variation. Label space is an implicit representation that offers unbiased algebraic manipulation and natural expression of label uncertainty. We demonstrate smoothing and registration on multi-label brain MRI. More... New: J. Malcolm, Y. Rathi, A. Tannenbaum. "Label Space: A Multi-Object Shape Representation." In Combinatorial Image Analysis, 2008. |
|
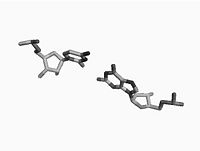
Non Parametric Clustering for Biomolecular Structural AnalysisHigh accuracy imaging and image processing techniques allow for collecting structural information of biomolecules with atomistic accuracy. Direct interpretation of the dynamics and the functionality of these structures with physical models, is yet to be developed. Clustering of molecular conformations into classes seems to be the first stage in recovering the formation and the functionality of these molecules. More... New: E. Hershkovits, A. Tannenbaum, and R. Tannenbaum. Adsorption of Block Copolymers from Selective Solvents on Curved Surfaces. Macromolecules. 2008. |
|
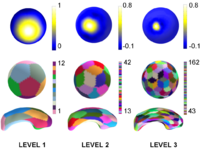
Multiscale Shape AnalysisWe present a novel method of statistical surface-based morphometry based on the use of non-parametric permutation tests and a spherical wavelet (SWC) shape representation. More... |
|
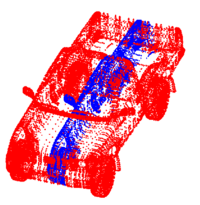
Point Set Rigid RegistrationIn this work, we propose a particle filtering approach for the problem of registering two point sets that differ by a rigid body transformation. Experimental results are provided that demonstrate the robustness of the algorithm to initialization, noise, missing structures or differing point densities in each sets, on challenging 2D and 3D registration tasks. More... New: R. Sandhu, S. Dambreville, A. Tannenbaum. Particle Filtering for Registration of 2D and 3D Point Sets with Stochastic Dynamics. In CVPR, 2008. |
|
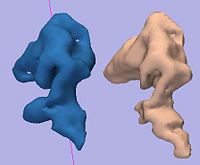
Rule-Based DLPFC SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex. More... |
|
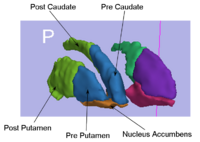
Rule-Based Striatum SegmentationIn this work, we provide software to semi-automate the implementation of segmentation procedures based on expert neuroanatomist rules for the striatum. More... New: Al-Hakim, et al. Parcellation of the Striatum. SPIE MI 2007. |
|
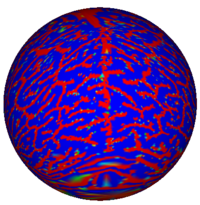
Conformal FlatteningThe goal of this project is for better visualizing and computation of neural activity from fMRI brain imagery. Also, with this technique, shapes can be mapped to shperes for shape analysis, registration or other purposes. Our technique is based on conformal mappings which map genus-zero surface: in fmri case cortical or other surfaces, onto a sphere in an angle preserving manner. More... |
Kernel PCA for SegmentationSegmentation performances using active contours can be drastically improved if the possible shapes of the object of interest are learnt. The goal of this work is to use Kernel PCA to learn shape priors. Kernel PCA allows for learning non linear dependencies in data sets, leading to more robust shape priors. More... New: S. Dambreville, Y. Rathi, and A. Tannenbaum. A Framework for Image Segmentation using Image Shape Models and Kernel PCA Shape Priors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2008 Aug;30(8):1385-99 | |
|
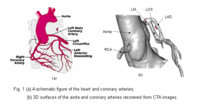
Blood Vessel SegmentationThe goal of this work is to develop blood vessel segmentation techniques for 3D MRI and CT data. The methods have been applied to coronary arteries and portal veins, with promising results. More... |
|
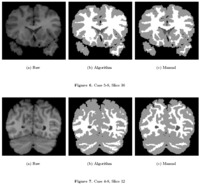
Knowledge-Based Bayesian SegmentationThis ITK filter is a segmentation algorithm that utilizes Bayes's Rule along with an affine-invariant anisotropic smoothing filter. More... |
|
Stochastic Methods for SegmentationNew stochastic methods for implementing curvature driven flows for various medical tasks such as segmentation. More... |
|
Automatic Outlining of sulci on the brain surfaceWe present a method to automatically extract certain key features on a surface. We apply this technique to outline sulci on the cortical surface of a brain. More... |
KPCA, LLE, KLLE Shape AnalysisThe goal of this work is to study and compare shape learning techniques. The techniques considered are Linear Principal Components Analysis (PCA), Kernel PCA, Locally Linear Embedding (LLE) and Kernel LLE. More... | |
|
Statistical/PDE Methods using Fast Marching for SegmentationThis Fast Marching based flow was added to Slicer 2. More... |