Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C08
From NAMIC Wiki
Home < Projects:RegistrationLibrary:RegLib C08
Back to ARRA main page
Back to Registration main page
Back to Registration Use-case Inventory
Contents
Slicer Registration Use Case Exampe #8: Intra-subject whole-body PET-CT
Objective / Background
Change assessment.
Keywords
PET-CT, whole-body, change assessment
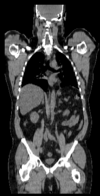
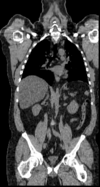
Input Data
 reference/fixed : baseline CT: 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm , PET: 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm
reference/fixed : baseline CT: 0.97 x 0.97 x 3.27 mm , PET: 4.7 x 4.7 x 3.3 mm moving: CT: 0.98 x 0.98 x 5
moving: CT: 0.98 x 0.98 x 5 moving: PET: 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm
moving: PET: 4.1 x 4.1 x 5 mm
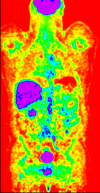
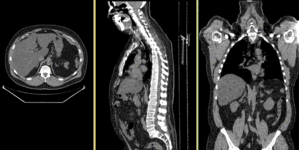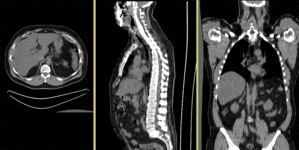
Registration Results
Download
Link to User Guide: How to Load/Save Registration Parameter Presets
Discussion: Registration Challenges
- accuracy is the critical criterion here. We need the registration error (residual misalignment) to be smaller than the change we want to measure/detect. Agreement on what constitutes good alignment can therefore vary greatly.
- the two series have different voxel sizes
- because of the large FOV we have strong non-rigid deformations from differences in patient/limb positions etc.
- images are large volumes (>100 MB total)
- image content reaches border of image on two sides
Discussion: Key Strategies
- the two images have identical contrast, hence we can consider "sharper" cost functions, such as NormCorr or MeanSqrd
- the contrast differences between the PET and CT far exceed the longitudinal differences in either modality. Hence, if necessary we can take advantage by registering each series separately and then build a concatenated transform.
- the two images are far apart initially, we will need some form of initialization. Manual alignment is a fast and effective approach for this.
- because accuracy is more important than speed here, we increase the sampling rate from the default 2% to 15%. Note however the large image size, which makes comparable sampling % still large compared to other datasets.