2012 Winter Project Week: Continuous 4D shapes
Key Investigators
James Fishbaugh, Hans Johnson, Guido Gerig
Objective
During the 2011 summer project week, we applied our shape regression framework to sub-cortical shapes from a single HD subject. For this project, we plan to begin processing multiple subjects. We would like to compare the trajectories of various measurements of interest, such as volume, across subjects at different stages of disease progression.
Approach, Plan
- Estimate continuous trajectories for sub-cortical structures for multiple subjects
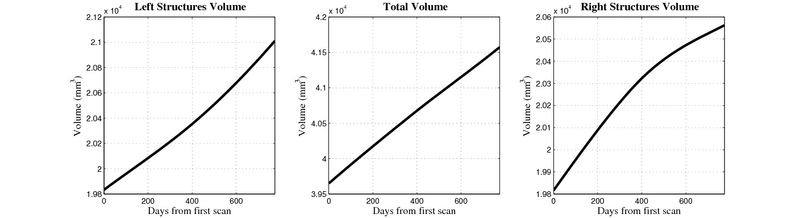
- Investigate volume changes between subjects at different stages of disease progression
- Explore shape evolution for other potentially significant measurements
Progress
Segmentation
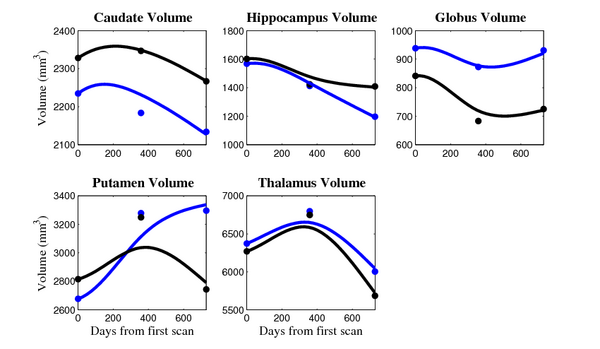
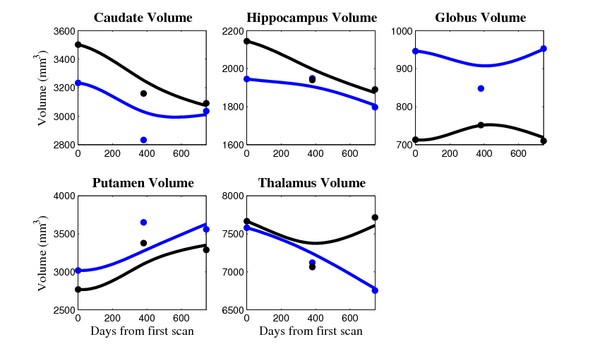
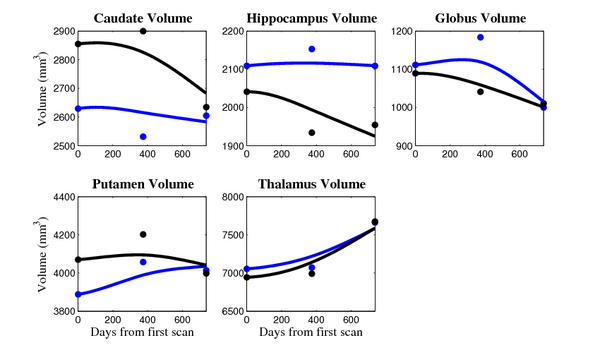
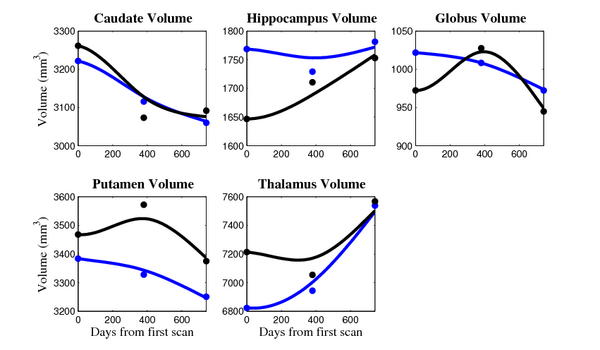
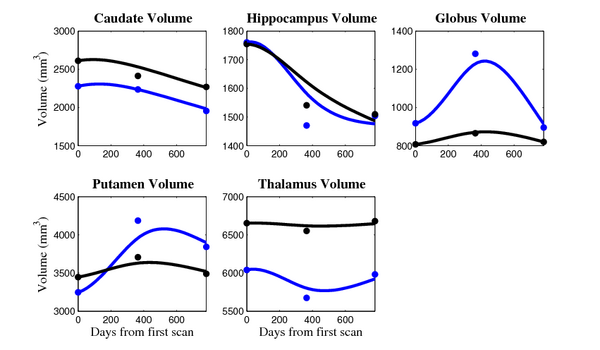
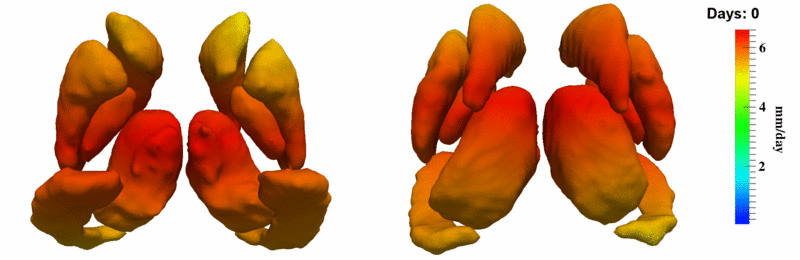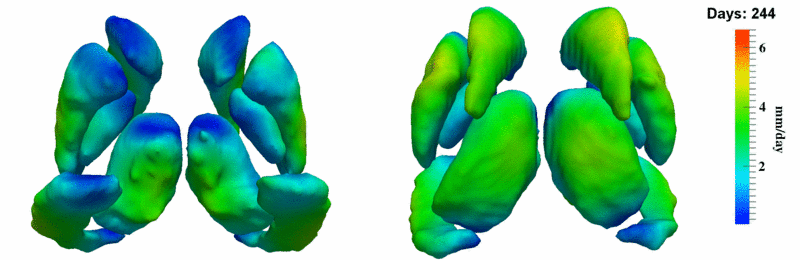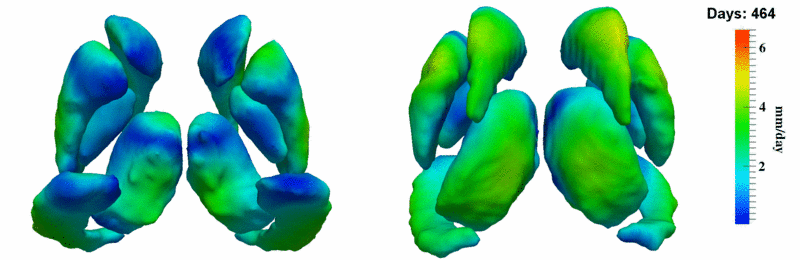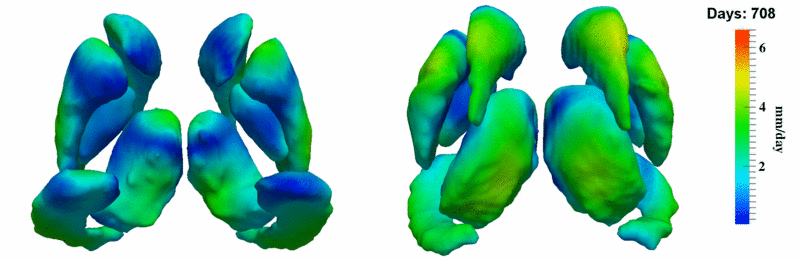
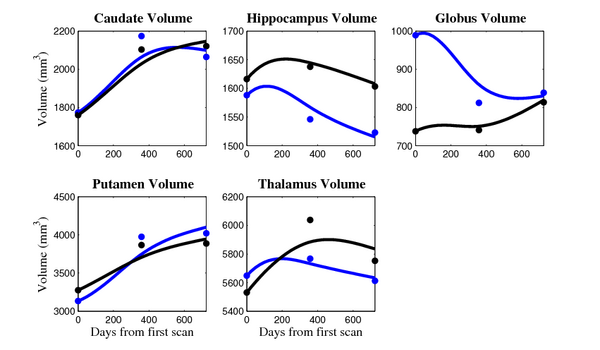
The 5 pairs of sub-cortical structures (caudate, hippocampus, globus, putamen, thalamus) segmentations were provided as binary images. Triangular meshes were extracted using marching cubes, giving us 10 shapes at 3 time points.
Preprocessing
In order to prepare the shapes for longitudinal regression, the different time points must first be rigidly aligned. We do not have point correspondences between our shapes, so we use a Gaussian mixture model based tool called gmmreg to rigidly align the shapes.
We initially align the entire shape complex, rather than individual shapes, in order to preserve the spatial relationship between the anatomical structures. However, there was a small amount of translation and rotation remaining after this process that adversely impacts the growth estimation. To further align the shapes, we also register each shape individually across time.
Regression
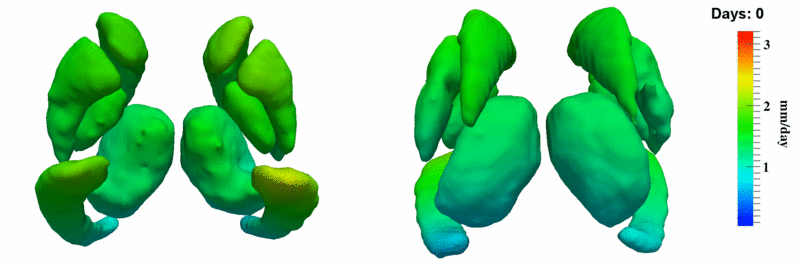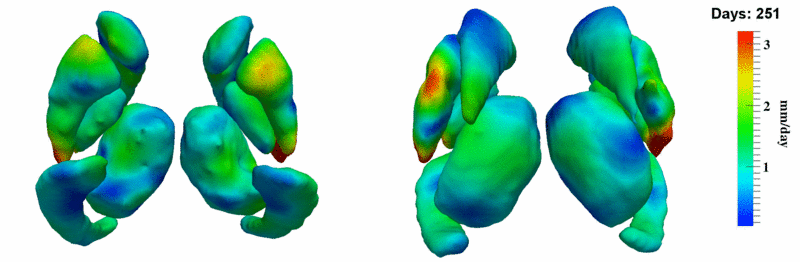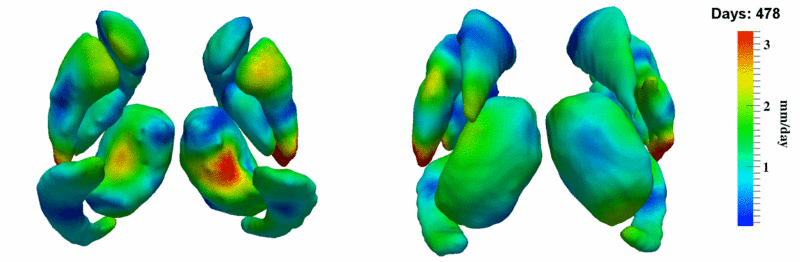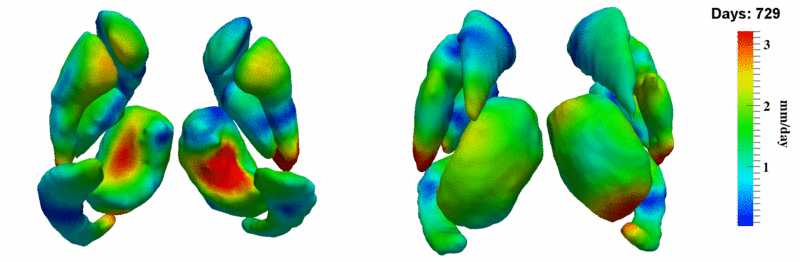
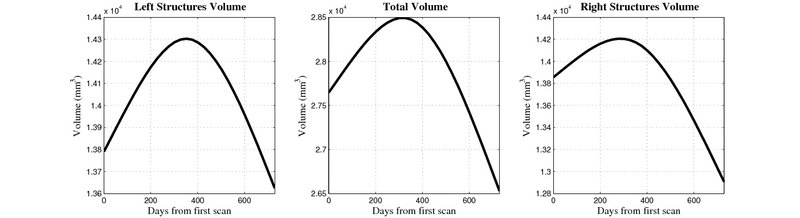
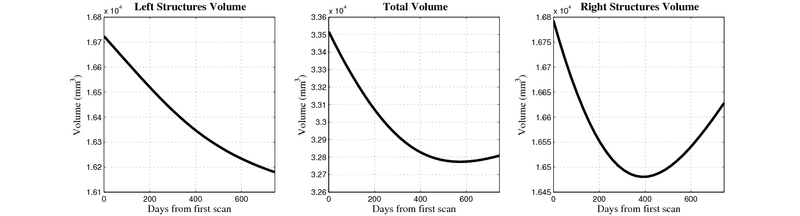
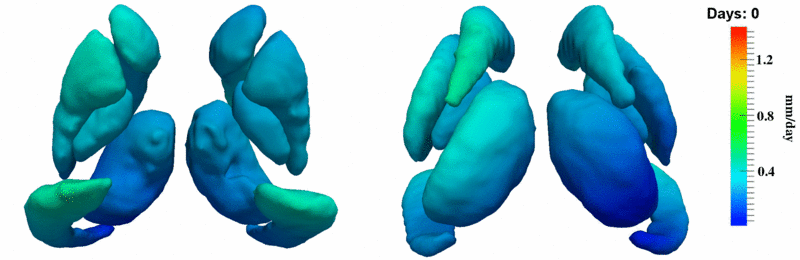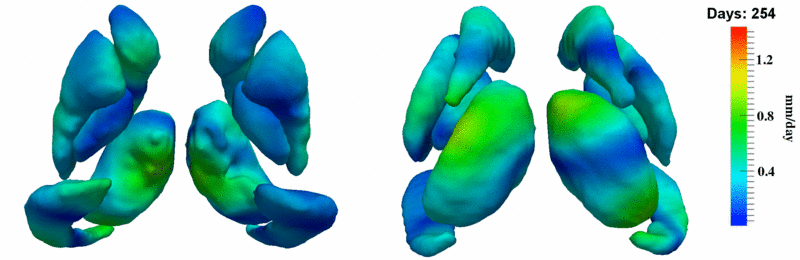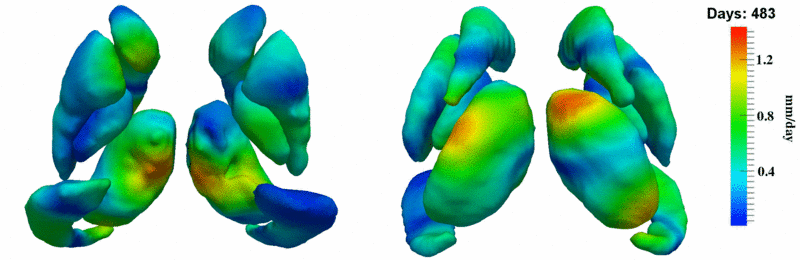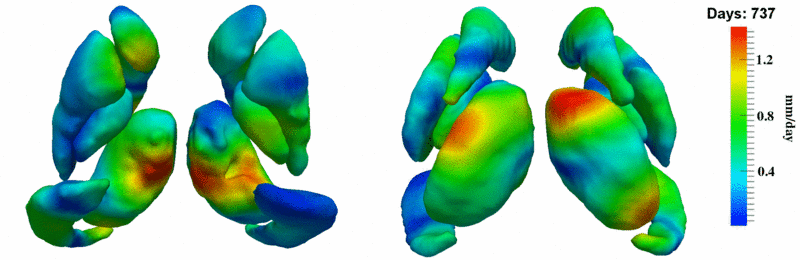
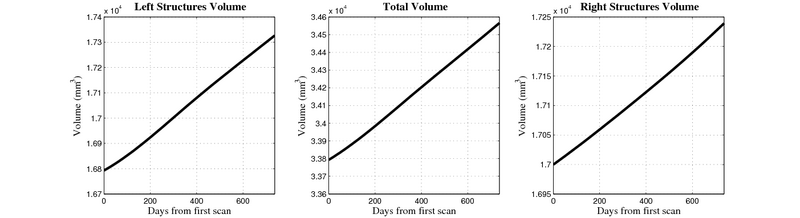
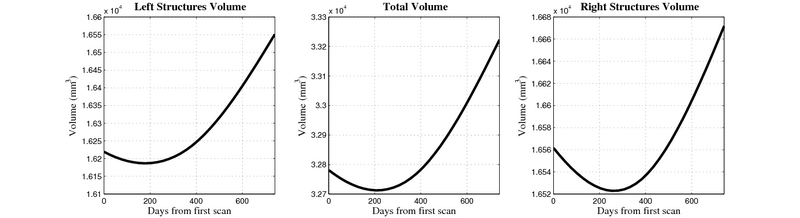
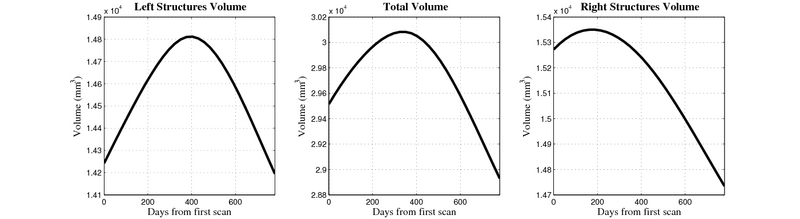
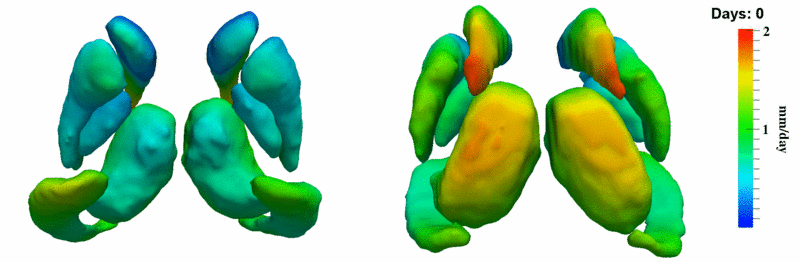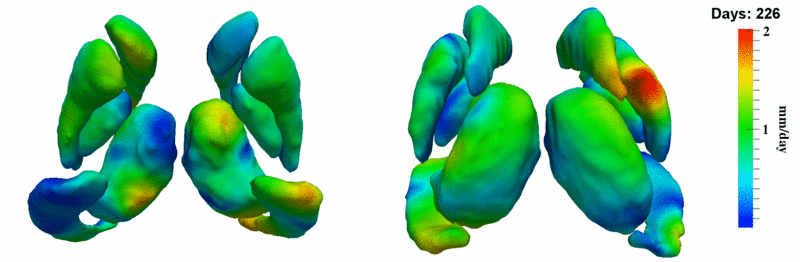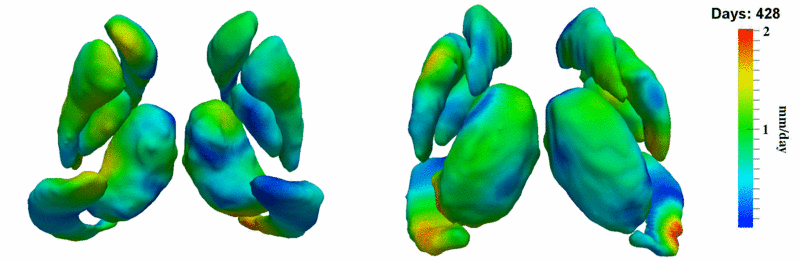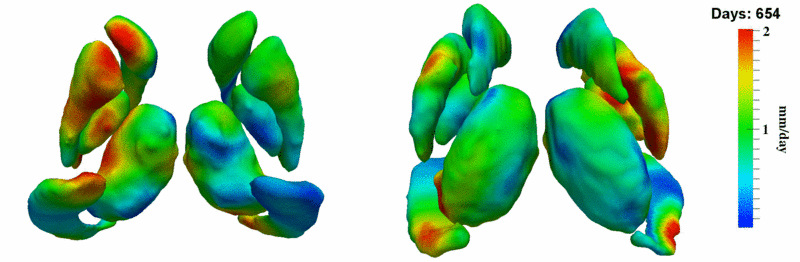
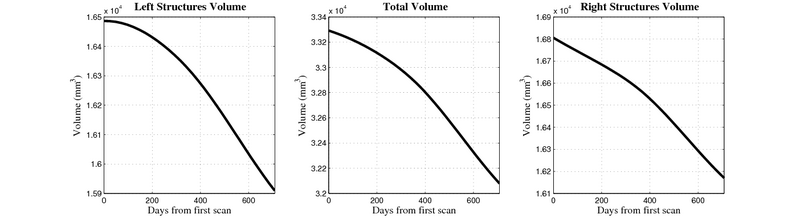
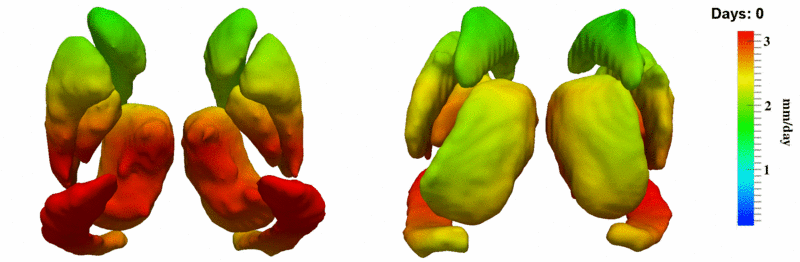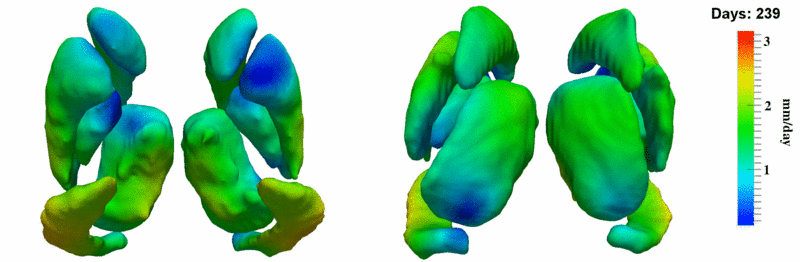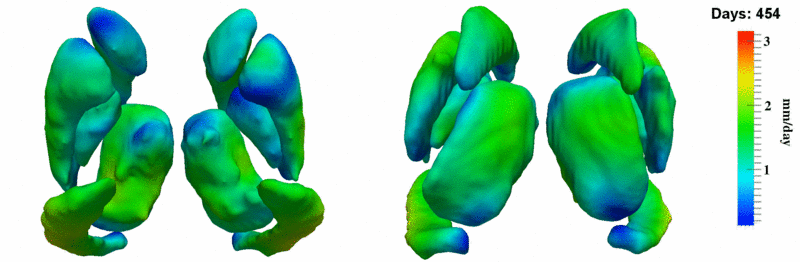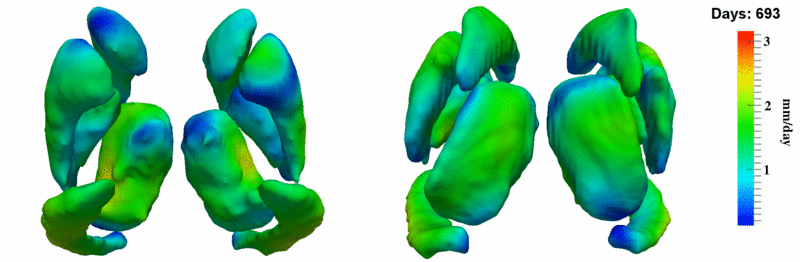
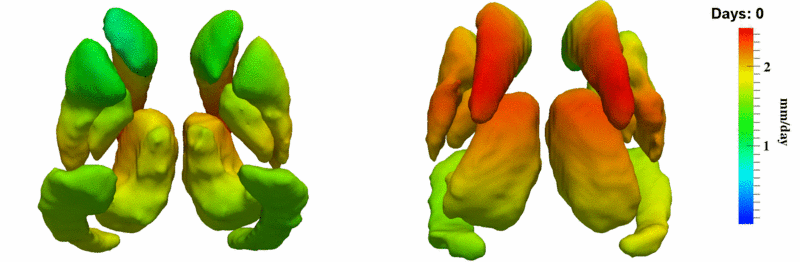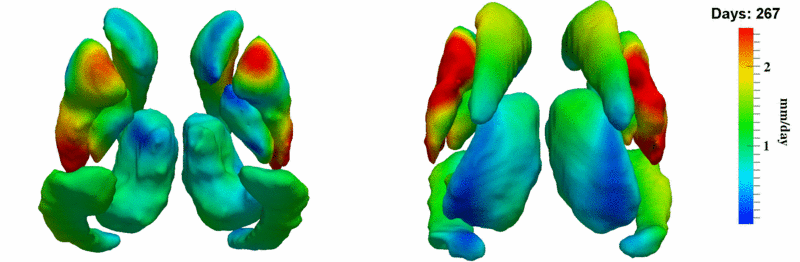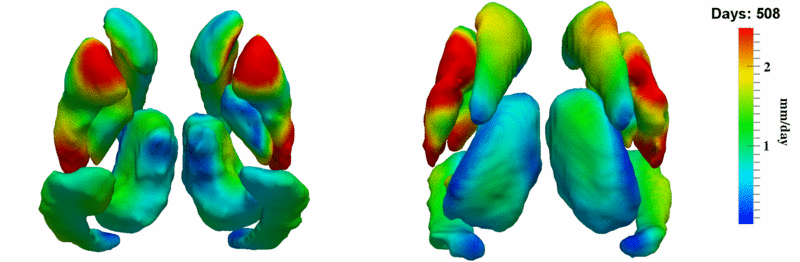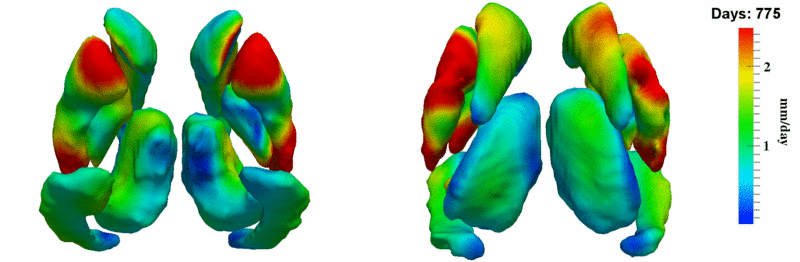
Here, we estimate the continuous evolution of all 10 structures as a shape complex. We look for a global deformation which best deforms the baseline shapes to match the target shapes over time. We set the spatial extent at which the deformation varies to 10mm.
Remarks
HD group
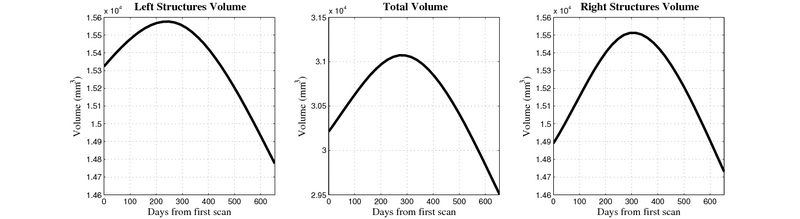
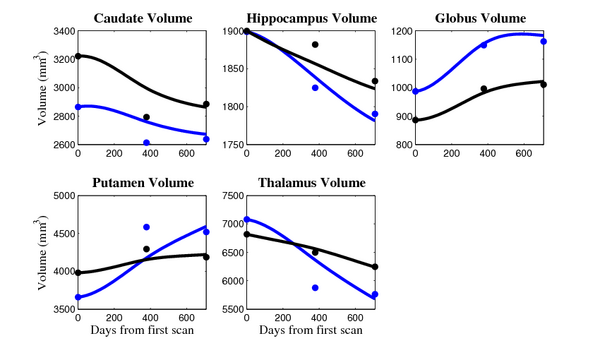
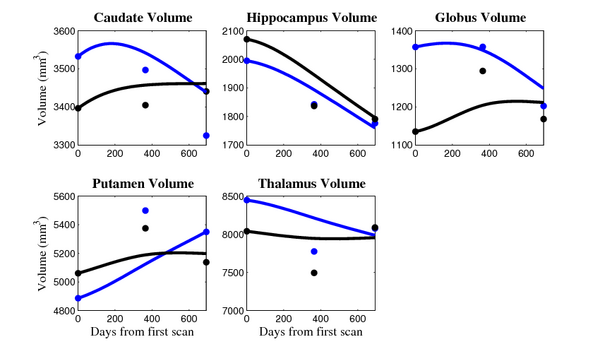
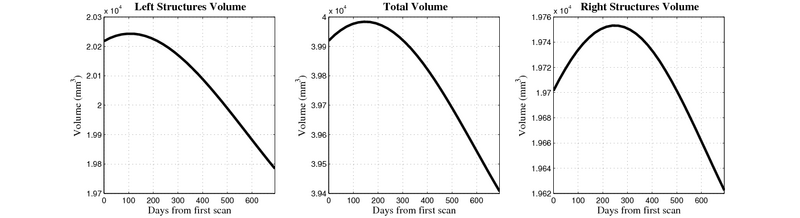
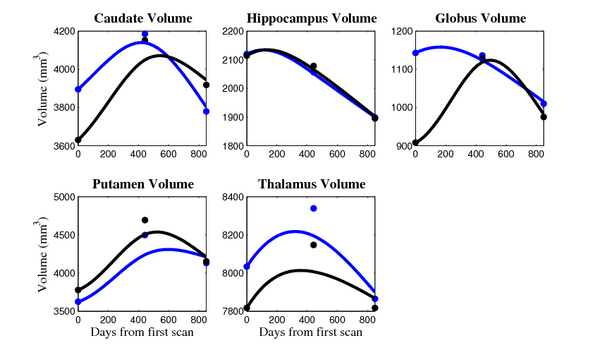
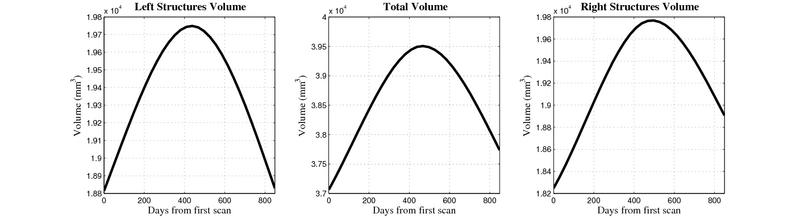
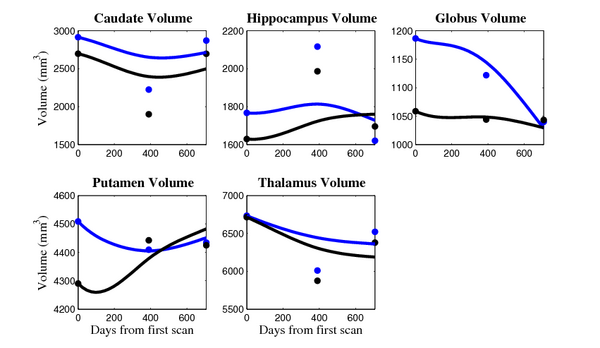
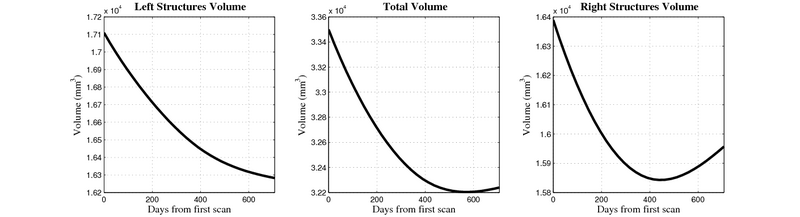
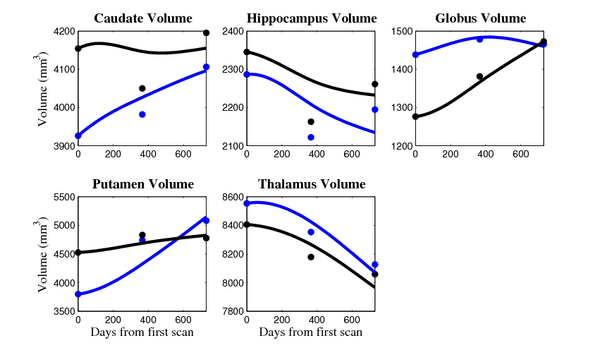
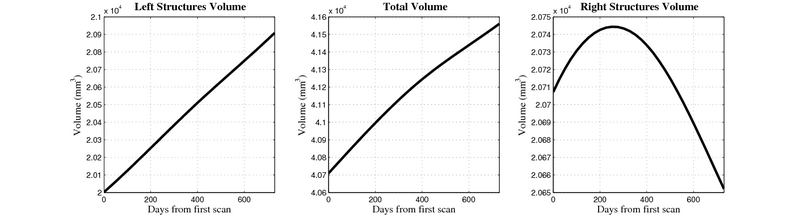
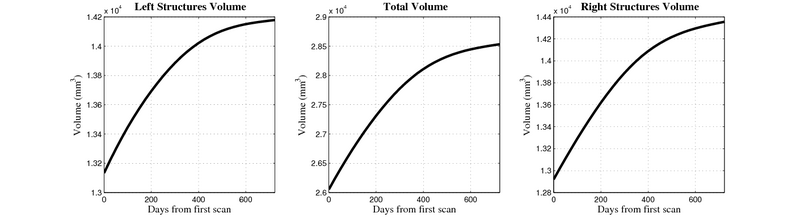
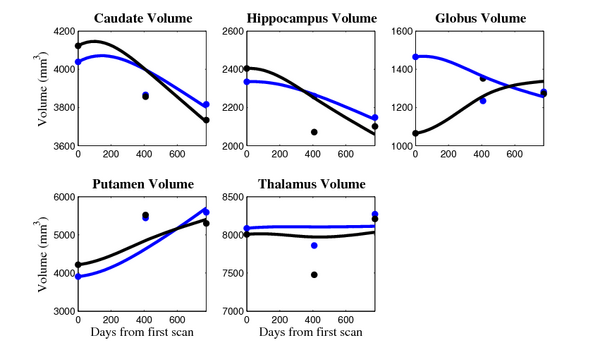
- Caudate volume decreases for all 6 subjects.
- Hippocampus volume decreases for 5 of 6 subjects.
- Typical changes are on the range of 5% to 10%
Control group
- Caudate volume decreases for 3 of 7 subjects.
- It is not uncommon to see a 10% decrease/increase in volume between time point in any given structure.
Conclusion
- We need to be very careful about the quality of the segmentations. The changes we are interested in detecting could potentially be of the same order as segmentation error.
- To improve the shape framework, we should estimate the baseline shape, which we currently assume is fixed.
- We still need to look for other potentially significant measurements, aside from volume.
HD Subjects
10001
10002
10010
10018
10022
10027
Control Subjects
10003
10004
10009
10014
10016
10017
10059
References
- Fishbaugh, J., Durrleman, S., Gerig, G. A Framework for Longitudinal Data Analysis via Shape Regression . SPIE Medical Imaging 2012: Image Processing. Vol. 8314. (To appear)
- Fishbaugh, J., Durrleman, S., Gerig, G. Estimation of Smooth Growth Trajectories with Controlled Acceleration from Time Series Shape Data. Proc. of Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI '11). September 2011.